Non-testosterone management of male hypogonadism: an examination of the existing literature
- PMID: 32257856
- PMCID: PMC7108991
- DOI: 10.21037/tau.2019.11.16
Non-testosterone management of male hypogonadism: an examination of the existing literature
Abstract
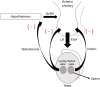
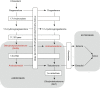
Testosterone deficiency is defined as a total testosterone level <300 ng/dL confirmed on two early morning lab draws. Testosterone therapy has historically been offered to men with symptomatic testosterone deficiency in the form of injections, gels, or pellets. However, these treatments are invasive or have undesirable effects including the risk of drug transference. Additionally, testosterone therapy has been associated with increases in hematocrit and controversy remains regarding the risk of cardiovascular and thromboembolic events while on testosterone therapy. As such, much interest has recently been focused on alternative treatment options for testosterone deficiency in the form of orally-administered medications with more favorable side effect profiles. Lifestyle modifications and varicocelectomy have been shown to raise endogenous testosterone production. Similarly, SERMs and aromatase inhibitors (AIs) have been shown to raise testosterone levels safely and effectively. Human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) remains the only FDA-approved non-testosterone treatment option for testosterone deficiency in men. However, this medication is expensive and requires patient-administered injections. Over the counter herbal supplements and designer steroids remain available though they are poorly studied and are associated with the potential for abuse as well as increased hepatic and cardiovascular risks. This review aims to discuss the existing treatment alternatives to traditional testosterone therapy, including efficacy, safety, and side effects of these options. The authors suggest that the SERM clomiphene citrate (CC) holds the greatest promise as a non-testosterone treatment option for testosterone deficiency.
Keywords: Aromatase inhibitors (AIs); gonadotropins; hypogonadism; selective estrogen receptor modulators (SERMs); testosterone.
2020 Translational Andrology and Urology. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The focused issue “Contemporary Issues and Controversies in Men’s Health” was commissioned by the editorial office without any funding or sponsorship. The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Clomiphene citrate and human chorionic gonadotropin are both effective in restoring testosterone in hypogonadism: a short-course randomized study.BJU Int. 2018 Nov;122(5):889-897. doi: 10.1111/bju.14401. Epub 2018 Jun 14. BJU Int. 2018. PMID: 29772111 Clinical Trial.
-
Testosterone supplementation versus clomiphene citrate for hypogonadism: an age matched comparison of satisfaction and efficacy.J Urol. 2014 Sep;192(3):875-9. doi: 10.1016/j.juro.2014.03.089. Epub 2014 Mar 21. J Urol. 2014. PMID: 24657837
-
Emerging medication for the treatment of male hypogonadism.Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. 2016 Sep;21(3):255-66. doi: 10.1080/14728214.2016.1226799. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. 2016. PMID: 27552127 Review.
-
Clomiphene citrate and testosterone gel replacement therapy for male hypogonadism: efficacy and treatment cost.J Sex Med. 2010 Jan;7(1 Pt 1):269-76. doi: 10.1111/j.1743-6109.2009.01454.x. Epub 2009 Aug 17. J Sex Med. 2010. PMID: 19694928
-
Treatment of hypogonadotropic male hypogonadism: Case-based scenarios.World J Nephrol. 2015 May 6;4(2):245-53. doi: 10.5527/wjn.v4.i2.245. World J Nephrol. 2015. PMID: 25949938 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative Study of the Steroidogenic Effects of Human Chorionic Gonadotropin and Thieno[2,3-D]pyrimidine-Based Allosteric Agonist of Luteinizing Hormone Receptor in Young Adult, Aging and Diabetic Male Rats.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Oct 11;21(20):7493. doi: 10.3390/ijms21207493. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33050653 Free PMC article.
-
ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction (STEMI) Due to Left Ventricular Thrombus Embolization: Implications of Multiagent Hormone Replacement Therapy.Cureus. 2025 Jan 5;17(1):e76951. doi: 10.7759/cureus.76951. eCollection 2025 Jan. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 39906442 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term use of clomiphene in male macroprolactinomas with persistent hypogonadism.Endocrine. 2024 Jul;85(1):152-157. doi: 10.1007/s12020-024-03817-0. Epub 2024 Apr 5. Endocrine. 2024. PMID: 38578401
-
Medical treatment prior to micro-TESE.Asian J Androl. 2025 May 1;27(3):342-354. doi: 10.4103/aja202492. Epub 2024 Dec 24. Asian J Androl. 2025. PMID: 39716721 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative Study of the Restoring Effect of Metformin, Gonadotropin, and Allosteric Agonist of Luteinizing Hormone Receptor on Spermatogenesis in Male Rats with Streptozotocin-Induced Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.Bull Exp Biol Med. 2022 Feb;172(4):435-440. doi: 10.1007/s10517-022-05409-2. Epub 2022 Feb 17. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2022. PMID: 35175480
References
-
- MacIndoe JH, Perry PJ, Yates WR, et al. Testosterone suppression of the HPT axis. J Investig Med 1997;45:441-7. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
