Role of glutathione redox system on the susceptibility to deoxynivalenol of pheasant (Phasianus colchicus)
- PMID: 32257930
- PMCID: PMC7099110
- DOI: 10.1007/s43188-019-00006-4
Role of glutathione redox system on the susceptibility to deoxynivalenol of pheasant (Phasianus colchicus)
Abstract
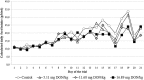
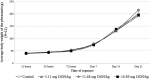
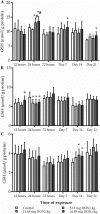
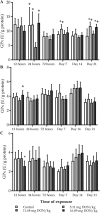
There are only a few reports on the effects of mycotoxins on pheasant (Phasianus colchicus) and the susceptibility to deoxynivalenol of these birds have never been reported before. The present experiment focuses to investigate the effects of different dietary concentrations of deoxynivalenol on blood plasma protein content, some parameters of lipid peroxidation and glutathione redox system and on the performance of pheasant chicks. A total of 320 1-day-old female pheasants were randomly assigned to four treatment groups fed with a diet contaminated with deoxynivalenol (control, 5.11 mg/kg, 11.68 mg/kg and 16.89 mg/kg). Birds were sacrificed at early (12, 24 and 72 h) and late (1, 2 and 3 weeks) stages of the experiment to demonstrate the oxidative stress-inducing effect of deoxynivalenol. Feed refusal was dose dependent, especially in the last third of the trial, but only minor body weight gain decrease was found. Lipid-peroxidation parameters did not show dose-dependent effect, except in blood plasma during the early stage of the trial. The glutathione redox system, reduced glutathione content and glutathione peroxidase activity, was activated in the liver, but primarily in the blood plasma. Glutathione peroxidase activity has changed parallel with reduced glutathione concentration in all tissues. Comparing our results with literature data, pheasants seem to have the same or higher tolerance to deoxynivalenol than other avian species, and glutathione redox system might contribute in some extent to this tolerance, as effective antioxidant defence against oxidative stress.
Keywords: Antioxidant defense; Glutathione peroxidase; Lipid peroxidation; Malondialdehyde; Reduced glutathione.
© The Author(s) 2019.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestNo potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors.
Figures
References
-
- Grove JF. Non-macrocyclic trichothecenes. Nat Prod Rep. 1988;5:187–209. - PubMed
-
- Grove JF. Non-macrocyclic trichothecenes (Part 2) Prog Chem Org Nat Prod. 2000;69:1–70.
-
- IPCS (1990) Environmental health criteria 105. Selected mycotoxins WHO, Vammala. II: Trichothecenes. pp 71–164
-
- CAST (2003) Mycotoxins: risks in plant, animal and human systems. Task force report no. 139. Council for Agriculture, Science and Technology, Ames, IA, pp 64–65
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

