Prevalence and Therapies of Antibiotic-Resistance in Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 32257966
- PMCID: PMC7089872
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.00107
Prevalence and Therapies of Antibiotic-Resistance in Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
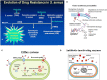
Infectious diseases are the second most important cause of human death worldwide; Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) is a very common human pathogenic microorganism that can trigger a variety of infectious diseases, such as skin and soft tissue infections, endocarditis, osteomyelitis, bacteremia, and lethal pneumonia. Moreover, according to the sensitivity to antibiotic drugs, S. aureus can be divided into methicillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus (MSSA) and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). In recent decades, due to the evolution of bacteria and the abuse of antibiotics, the drug resistance of S. aureus has gradually increased, the infection rate of MRSA has increased worldwide, and the clinical anti-infective treatment for MRSA has become more difficult. Accumulating evidence has demonstrated that the resistance mechanisms of S. aureus are very complex, especially for MRSA, which is resistant to many kinds of antibiotics. Therefore, understanding the drug resistance of MRSA in a timely manner and elucidating its drug resistance mechanism at the molecular level are of great significance for the treatment of S. aureus infection. A large number of researchers believe that analyzing the molecular characteristics of S. aureus can help provide a basis for designing effective prevention and treatment measures against hospital infections caused by S. aureus and further monitor the evolution of S. aureus. This paper reviews the research status of MSSA and MRSA, the detailed mechanisms of the intrinsic antibiotic resistance and the acquired antibiotic resistance, the advanced research on anti-MRSA antibiotics and novel therapeutic strategies for MRSA treatment.
Keywords: Staphylococcus aureus; acquired antibiotic resistance; antibiotic resistance therapy; cell membrane; molecular mechanisms.
Copyright © 2020 Guo, Song, Sun, Wang and Wang.
Figures
References
-
- Andrade J. C., Morais-Braga M. F., Guedes G. M., Tintino S. R., Freitas M. A., Menezes I. R., et al. (2014). Enhancement of the antibiotic activity of aminoglycosides by alpha-tocopherol and other cholesterol derivates. Biomed. Pharmacother. 68, 1065–1069. 10.1016/j.biopha.2014.10.011 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

