Essential Metabolic Routes as a Way to ESKAPE From Antibiotic Resistance
- PMID: 32257985
- PMCID: PMC7093009
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2020.00026
Essential Metabolic Routes as a Way to ESKAPE From Antibiotic Resistance
Abstract
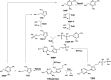
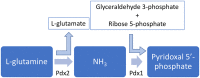
Antibiotic resistance is a worldwide concern that requires a concerted action from physicians, patients, governmental agencies, and academia to prevent infections and the spread of resistance, track resistant bacteria, improve the use of current antibiotics, and develop new antibiotics. Despite the efforts spent so far, the current antibiotics in the market are restricted to only five general targets/pathways highlighting the need for basic research focusing on the discovery and evaluation of new potential targets. Here we interrogate two biosynthetic pathways as potentially druggable pathways in bacteria. The biosynthesis pathway for thiamine (vitamin B1), absent in humans, but found in many bacteria, including organisms in the group of the ESKAPE pathogens (Enterococcus faecium, Staphylococcus aureus, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Acinetobacter baumanii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Enterobacter sp.) and the biosynthesis pathway for pyridoxal 5'-phosphate and its vitamers (vitamin B6), found in S. aureus. Using current genomic data, we discuss the possibilities of inhibition of enzymes in the pathway and review the current state of the art in the scientific literature.
Keywords: ESKAPE pathogens; antibiotic resistance; pyridoxal 5′-phosphate; thiamine; vitamin biosynthesis.
Copyright © 2020 Barra, Dantas, Morão, Gutierrez, Polikarpov, Wrenger and Nascimento.
Figures
References
-
- CDC Antibiotic Resistance Threats in the USA. Atlanta, GA: CDC; (2013).
-
- WHO Prioritization of Pathogens to Guide Discovery, Research and Development of New Antibiotics for Drug-Resistant Bacterial Infections, Including Tuberculosis. Geneva: WHO; (2017).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases