Antioxidant Nanotherapies for the Treatment of Inflammatory Diseases
- PMID: 32258013
- PMCID: PMC7093330
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2020.00200
Antioxidant Nanotherapies for the Treatment of Inflammatory Diseases
Abstract
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are essential in regulating various physiological functions. However, overproduction of ROS is implicated in the pathogenesis of various inflammatory diseases. Antioxidant therapy has thus represented an effective strategy for the treatment of oxidative stress relevant inflammatory diseases. Conventional anti-oxidative agents showed limited in vivo effects owing to their non-specific distribution and low retention in disease sites. Over the past decades, significant achievements have been made in the development of antioxidant nanotherapies that exhibit multiple advantages such as excellent pharmacokinetics, stable anti-oxidative activity, and intrinsic ROS-scavenging properties. This review provides a comprehensive overview on recent advances in antioxidant nanotherapies, including ROS-scavenging inorganic nanoparticles, organic nanoparticles with intrinsic antioxidant activity, and drug-loaded anti-oxidant nanoparticles. We highlight the biomedical applications of antioxidant nanotherapies in the treatment of different inflammatory diseases, with an emphasis on inflammatory bowel disease, cardiovascular disease, and brain diseases. Current challenges and future perspectives to promote clinical translation of antioxidant nanotherapies are also briefly discussed.
Keywords: ROS; antioxidant nanotherapies; inflammatory diseases; nanoparticles; oxidative stress.
Copyright © 2020 Li, Li, Chen, Zhang and Lu.
Figures
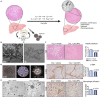
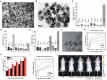

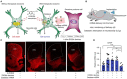
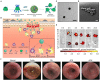
References
-
- Alexescu T., Tarmure S., Negrean V., Cosnarovici M., Ruta V., Popovici I., et al. (2019). Nanoparticles in the treatment of chronic lung diseases. J. Mind Med. Sci. 6, 224–231. 10.22543/7674.62.P224231 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

