Patient-Specific or Conventional Instrumentations: A Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
- PMID: 32258107
- PMCID: PMC7085852
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/2164371
Patient-Specific or Conventional Instrumentations: A Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Abstract
Objective: To conduct a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) to compare knee arthroplasty with patient-specific instrumentation (PSI) with the conventional instrumentation (CI).
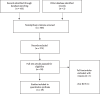
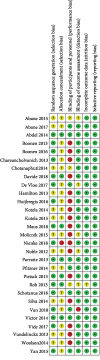
Methods: RCTs were selected in PubMed and Embase from 2012 to 2018. Key data extracted included malalignment of mechanical axis, blood loss, surgical time, Oxford Knee Score (OKS), Knee Society Score (KSS), length of stay, and complications. Subgroup analysis was also performed regarding different PSI systems and different image processing methods.
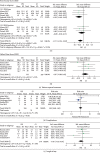
Results: 29 RCTs with 2487 knees were eligible for the meta-analysis. Results showed that PSI did not improve the alignment of the mechanical axis compared with CI, but MRI-based PSI and Visionaire-specific PSI decrease the risk of malalignment significantly (P = 0.04 and P = 0.04 and P = 0.04 and P = 0.04 and P = 0.04 and.
Conclusion: PSI reduced the blood loss and improved KSS. MRI-based PSI reduced operative time and risk of malalignment of mechanical axis compared with CT-based PSI. Moreover, Visionaire-specific PSI achieves better alignment result of the mechanical axis than other systems.
Copyright © 2020 Yipeng Lin et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Patient-specific instrumentation improved mechanical alignment, while early clinical outcome was comparable to conventional instrumentation in TKA.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2016 Jan;24(1):102-11. doi: 10.1007/s00167-014-3345-2. Epub 2014 Oct 19. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2016. PMID: 25326759
-
Patient-specific instrumentation improved axial alignment of the femoral component, operative time and perioperative blood loss after total knee arthroplasty.Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2019 Apr;27(4):1083-1095. doi: 10.1007/s00167-018-5256-0. Epub 2018 Oct 30. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2019. PMID: 30377714 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparison of clinical outcomes of VISIONAIRE patient-specific instrumentation with conventional instrumentation in total knee arthroplasty: a systematic literature review and meta-analysis.Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2023 Jul;143(7):4379-4393. doi: 10.1007/s00402-022-04698-6. Epub 2022 Nov 30. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2023. PMID: 36449066 Free PMC article.
-
Patient-specific instrumentation does not improve radiographic alignment or clinical outcomes after total knee arthroplasty.Acta Orthop. 2016 Aug;87(4):386-94. doi: 10.1080/17453674.2016.1193799. Epub 2016 Jun 1. Acta Orthop. 2016. PMID: 27249110 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional outcomes in patient specific instrumentation vs. conventional instrumentation for total knee arthroplasty; a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective studies.BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022 Jul 23;23(1):702. doi: 10.1186/s12891-022-05620-2. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2022. PMID: 35870913 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Patient-specific instrumentation (PSI) in total ankle arthroplasty: a systematic review.Int Orthop. 2021 Sep;45(9):2445-2452. doi: 10.1007/s00264-021-05145-8. Epub 2021 Aug 4. Int Orthop. 2021. PMID: 34345975
-
Knee Prosthesis in the Computer Era.Orthop Surg. 2021 Apr;13(2):395-401. doi: 10.1111/os.12762. Epub 2021 Jan 27. Orthop Surg. 2021. PMID: 33506615 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Study of Surgical Accuracy with X-Ray-Based Patient-Specific Instrument (X3DPSI®) vs Conventional Instrument in Total Knee Arthroplasty Surgeries.Indian J Orthop. 2022 Apr 5;56(7):1240-1250. doi: 10.1007/s43465-022-00623-6. eCollection 2022 Jul. Indian J Orthop. 2022. PMID: 35813546 Free PMC article.
-
[The importance of individual knee arthroplasty].Orthopadie (Heidelb). 2025 Sep;54(9):700-707. doi: 10.1007/s00132-025-04688-7. Epub 2025 Aug 7. Orthopadie (Heidelb). 2025. PMID: 40775457 Review. German.
-
Funding has no effect on clinical outcomes of total joint arthroplasty emerging technologies: a systematic review of bibliometrics and conflicts of interest.Arthroplasty. 2022 Nov 1;4(1):45. doi: 10.1186/s42836-022-00146-3. Arthroplasty. 2022. PMID: 36316729 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

