Evaluation of X-Ray Repair Cross-Complementing Family Members as Potential Biomarkers for Predicting Progression and Prognosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- PMID: 32258128
- PMCID: PMC7103035
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/5751939
Evaluation of X-Ray Repair Cross-Complementing Family Members as Potential Biomarkers for Predicting Progression and Prognosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
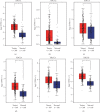
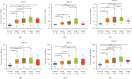
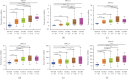
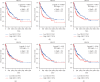
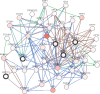
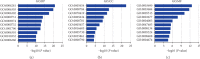
The X-ray repair cross-complementing (XRCC) gene family has been revealed to participate in the carcinogenesis and development of numerous cancers. However, the expression profiles and prognostic values of XRCCs (XRCC1-6) in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) have not been explored up to now. The transcriptional levels of XRCCs in primary HCC tissues were analyzed by UALCAN and GEPIA. The relationship between XRCCs expression and HCC clinical characteristics was evaluated using UALCAN. Moreover, the prognostic values of XRCCs expression and mutations in HCC patients were investigated via the GEPIA and cBioPortal, respectively. Last but not least, the functions and pathways of XRCCs in HCC were also predicted by cBioPortal and DVAID. The transcriptional levels of all XRCCs in HCC tissues were notably elevated compared with normal liver tissues. Meanwhile, upregulated XRCCs expression was positively associated with clinical stages and tumor grades of HCC patients. Survival analysis using the GEPIA database revealed that high transcription levels of XRCC2/3/4/5/6 were associated with lower overall survival (OS) and high transcription levels of XRCC1/2/3/6 were correlated with poor disease-free survival (DFS) in HCC patients. Furthermore, Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) demonstrated the possible mechanisms of XRCCs and their associated genes participating in the oncogenesis of HCC. Our findings systematically elucidate the expression profiles and distinct prognostic values of XRCCs in HCC, which might provide promising therapeutic targets and novel prognostic biomarkers for HCC patients.
Copyright © 2020 Jie Mei et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest relevant to this study.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Gene expression and prognosis of x-ray repair cross-complementing family members in non-small cell lung cancer.Bioengineered. 2021 Dec;12(1):6210-6228. doi: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1964193. Bioengineered. 2021. PMID: 34486486 Free PMC article.
-
Screening Hub Genes as Prognostic Biomarkers of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Bioinformatics Analysis.Cell Transplant. 2019 Dec;28(1_suppl):76S-86S. doi: 10.1177/0963689719893950. Epub 2019 Dec 11. Cell Transplant. 2019. PMID: 31822116 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying hepatocellular carcinoma-related hub genes by bioinformatics analysis and CYP2C8 is a potential prognostic biomarker.Gene. 2019 May 25;698:9-18. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2019.02.062. Epub 2019 Feb 27. Gene. 2019. PMID: 30825595
-
Systematic summarization of the expression profiles and prognostic roles of the dishevelled gene family in hepatocellular carcinoma.Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2020 Sep;8(9):e1384. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.1384. Epub 2020 Jun 26. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2020. PMID: 32588988 Free PMC article.
-
A meta-analysis for C-X-C chemokine receptor type 4 as a prognostic marker and potential drug target in hepatocellular carcinoma.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015 Jul 15;9:3625-33. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S86032. eCollection 2015. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2015. PMID: 26203228 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Construction of a 6-gene prognostic signature to assess prognosis of patients with pancreatic cancer.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Sep 11;99(37):e22092. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000022092. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 32925750 Free PMC article.
-
XRCC2 driven homologous recombination subtypes and therapeutic targeting in lung adenocarcinoma metastasis.NPJ Precis Oncol. 2024 Aug 1;8(1):169. doi: 10.1038/s41698-024-00658-y. NPJ Precis Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39090304 Free PMC article.
-
Construction of a nine DNA repair-related gene prognostic classifier to predict prognosis in patients with endometrial carcinoma.BMC Cancer. 2021 Jan 6;21(1):29. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-07712-5. BMC Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33407221 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of emodin in treating hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma: network pharmacology and cell experiments.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Sep 13;14:1458913. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1458913. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39346898 Free PMC article.
-
Association of XRCC1 Gene Polymorphism with an Increased Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in the Peshawar Population.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2025 Jun 1;26(6):2109-2115. doi: 10.31557/APJCP.2025.26.6.2109. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2025. PMID: 40542773 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

