Efficacy of Altered Two-Point Fixation in Zygomaticomaxillary Complex Fracture
- PMID: 32258152
- PMCID: PMC7103990
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/8537345
Efficacy of Altered Two-Point Fixation in Zygomaticomaxillary Complex Fracture
Abstract
Purpose: To reconstruct a zygomaticomaxillary complex (ZMC) fracture, zygomaticofrontal (ZF) suture is the most reliable site to assess anatomical alignment and to secure rigidity. It has been chosen primary site to be fixed, but approach through the lateral eyebrow incision may leave a visible scar. This study suggests altered two-point fixation of ZMC fracture without accessing the ZF suture.
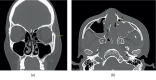
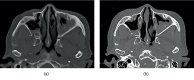
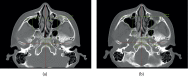
Methods: In the retrospective study, a total of 40 patients with ZMC fracture were divided into two groups (group 1, two-point fixation and group 2, three-point fixation). Patient demographics and follow-up were evaluated, and degree of reduction including cortical gaps of ZF and inferior orbital (IO) area, protruding difference of zygoma, and malar difference using asymmetry index were measured through preoperative and postoperative CT.
Results: Preoperatively, the means of ZF displacement, IO displacement, protruding difference of zygoma, and facial asymmetry index between the groups were not statistically different. The result was the same after the operation. However, all variables were significantly different before and after surgery within each group. Moreover, mean operation time was significantly different between groups (P value = 0.026).
Conclusion: Altered two-point fixation in ZMC fracture excluding incision approaching the ZF provides surgical efficacy and similar surgical outcomes to three-point fixation but offers reduced operation time and fewer complications.
Copyright © 2020 Jun Hyeok Kim et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Feasibility of 4-point fixation using the preauricular approach in a zygomaticomaxillary complex fracture.J Craniofac Surg. 2013 Mar;24(2):557-62. doi: 10.1097/SCS.0b013e3182700d23. J Craniofac Surg. 2013. PMID: 23524741
-
Radiological evaluation of sphenozygomatic suture fixation for restoration of orbital volume: A retrospective study.J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2016 Dec;44(12):1903-1908. doi: 10.1016/j.jcms.2016.10.007. Epub 2016 Oct 20. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2016. PMID: 27890546
-
The effectiveness of 1-point fixation for zygomaticomaxillary complex fractures.Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2012 Sep;138(9):828-32. doi: 10.1001/archoto.2012.1815. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2012. PMID: 22986716
-
A comparison of combinations of titanium and resorbable plating systems for repair of isolated zygomatic fractures in the adult: a quantitative biomechanical study.Ann Plast Surg. 2005 Apr;54(4):402-8. doi: 10.1097/01.sap.0000151484.59846.62. Ann Plast Surg. 2005. PMID: 15785282 Review.
-
Comparative evaluation of 2-point vs 3-point fixation in the treatment of zygomaticomaxillary complex fractures - A systematic review.J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2019 Oct;47(10):1542-1550. doi: 10.1016/j.jcms.2019.07.009. Epub 2019 Jul 19. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2019. PMID: 31395419
Cited by
-
Management of zygomatico maxillary complex fractures.Bioinformation. 2023 Jan 31;19(1):120-125. doi: 10.6026/97320630019120. eCollection 2023. Bioinformation. 2023. PMID: 37720278 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of 3 and 2-point internal fixation in the management of zygomaticomaxillary complex fractures: Case report.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2021 Jul 3;67:102539. doi: 10.1016/j.amsu.2021.102539. eCollection 2021 Jul. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2021. PMID: 34276986 Free PMC article.
-
Two-Point Versus Three-Point Fixation in Zygomaticomaxillary Complex (ZMC) Fractures: A Narrative Review.Cureus. 2025 Jun 9;17(6):e85659. doi: 10.7759/cureus.85659. eCollection 2025 Jun. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40642666 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Two-Point versus Three-Point Fixation in the Management of Zygomaticomaxillary Complex Fractures: A Comparative Study.Ann Maxillofac Surg. 2021 Jul-Dec;11(2):229-235. doi: 10.4103/ams.ams_75_20. Epub 2021 Dec 6. Ann Maxillofac Surg. 2021. PMID: 35265490 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

