Quality of Life in Patients with Morphea: A Cross-Sectional Study and a Review of the Current Literature
- PMID: 32258158
- PMCID: PMC7094194
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/9186274
Quality of Life in Patients with Morphea: A Cross-Sectional Study and a Review of the Current Literature
Abstract
Objective: The aim of the study was to evaluate QoL in patients suffering from morphea. Material and Methods. Sixty-five patients with morphea were recruited into this cross-sectional, prospective parallel study. QoL among adult patients was assessed with the Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI) and Euro-QoL-5D questionnaire; patients aged <17 years used the Children's Dermatology Life Quality Index (CDLQI). The severity of morphea was assessed using the Localized Scleroderma Cutaneous Assessment Tool. The results of QoL and its association with disease severity were compared between patients with various morphea subtypes.
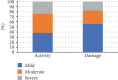
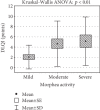
Results: The mean DLQI scoring was 3.8 ± 4.1 points and the CDLQI was 2.3 ± 3.0. The mean value of Visual Analogue Scale thermometer (EQ VAS) was 66.9 ± 17.5 points. The disease activity of morphea based on mLoSSI correlated significantly with QoL impairment according to the DLQI (R = 0.41, p = 0.001). No significant correlation was observed between morphea-induced damage and QoL (p = 0.99).
Conclusions: Evaluation of QoL in patients with morphea is still challenging due to lack of good assessment tools dedicated specifically for morphea patients. In general, QoL in morphea patients is significantly correlated with the disease activity, but not with disease-induced skin damage.
Copyright © 2020 Justyna Szczęch et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Fett N., Werth V. P. Update on morphea: part I. Epidemiology, clinical presentation, and pathogenesis. Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. 2011;64(2):217–228. - PubMed
-
- Knobler R., Moinzadeh P., Hunzelmann N., et al. European Dermatology Forum S1-guideline on the diagnosis and treatment of sclerosing diseases of the skin, part 1: localized scleroderma, systemic sclerosis and overlap syndromes. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology. 2017;31(9):1401–1424. doi: 10.1111/jdv.14458. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical