Inhibition of the Ubiquitin-Activating Enzyme UBA1 Suppresses Diet-Induced Atherosclerosis in Apolipoprotein E-Knockout Mice
- PMID: 32258175
- PMCID: PMC7109586
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/7812709
Inhibition of the Ubiquitin-Activating Enzyme UBA1 Suppresses Diet-Induced Atherosclerosis in Apolipoprotein E-Knockout Mice
Abstract
Background: Ubiquitin-like modifier activating enzyme 1 (UBA1) is the first and major E1 activating enzyme in ubiquitin activation, the initial step of the ubiquitin-proteasome system. Defects in the expression or activity of UBA1 correlate with several neurodegenerative and cardiovascular disorders. However, whether UBA1 contributes to atherosclerosis is not defined.
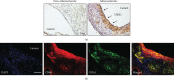
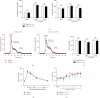
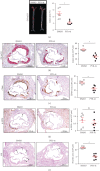
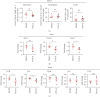
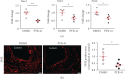
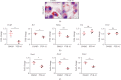
Methods and results: Atherosclerosis was induced in apolipoprotein E-knockout (Apoe-/-) mice fed on an atherogenic diet. UBA1 expression, detected by immunohistochemical staining, was found to be significantly increased in the atherosclerotic plaques, which confirmed to be mainly derived from lesional CD68+ macrophages via immunofluorescence costaining. Inactivation of UBA1 by the specific inhibitor PYR-41 did not alter the main metabolic parameters during atherogenic diet feeding but suppressed atherosclerosis development with less macrophage infiltration and plaque necrosis. PYR-41 did not alter circulating immune cells determined by flow cytometry but significantly reduced aortic mRNA levels of cytokines related to monocyte recruitment (Mcp-1, Vcam-1, and Icam-1) and macrophage proinflammatory responses (Il-1β and Il-6). Besides, PYR-41 also suppressed aortic mRNA expression of NADPH oxidase (Nox1, Nox2, and Nox4) and lesional oxidative stress levels, determined by DHE staining. In vitro, PYR-41 blunted ox-LDL-induced lipid deposition and expression of proinflammatory cytokines (Il-1β and Il-6) and NADPH oxidases (Nox1, Nox2, and Nox4) in cultured RAW264.7 macrophages.
Conclusions: We demonstrated that UBA1 expression was upregulated and mainly derived from macrophages in the atherosclerotic plaques and inactivation of UBA1 by PYR-41 suppressed atherosclerosis development probably through inhibiting macrophage proinflammatory response and oxidative stress. Our data suggested that UBA1 might be explored as a potential pharmaceutical target against atherosclerosis.
Copyright © 2020 Jiawei Liao et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Administration of ubiquitin-activating enzyme UBA1 inhibitor PYR-41 attenuates angiotensin II-induced cardiac remodeling in mice.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018 Oct 20;505(1):317-324. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.09.100. Epub 2018 Sep 22. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018. PMID: 30249396
-
The ubiquitin-activating enzyme E1 as a novel therapeutic target for the treatment of restenosis.Atherosclerosis. 2016 Apr;247:142-53. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2016.02.016. Epub 2016 Feb 13. Atherosclerosis. 2016. PMID: 26919560
-
Ubiquitin-like modifier-activating enzyme 1 as a potential therapeutic target for aortic dissection.Int Immunopharmacol. 2025 Jan 3;145:113742. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.113742. Epub 2024 Dec 4. Int Immunopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39637577
-
Ubiquitin-activating enzyme (UBA1) is required for sperm capacitation, acrosomal exocytosis and sperm-egg coat penetration during porcine fertilization.Int J Androl. 2012 Apr;35(2):196-210. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2605.2011.01217.x. Epub 2011 Sep 27. Int J Androl. 2012. PMID: 21950462
-
Teneligliptin, a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, attenuated pro-inflammatory phenotype of perivascular adipose tissue and inhibited atherogenesis in normoglycemic apolipoprotein-E-deficient mice.Vascul Pharmacol. 2017 Sep;96-98:19-25. doi: 10.1016/j.vph.2017.03.003. Epub 2017 Mar 27. Vascul Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28347868
Cited by
-
Cysteine-Rich LIM-Only Protein 4 (CRP4) Promotes Atherogenesis in the ApoE-/- Mouse Model.Cells. 2022 Apr 17;11(8):1364. doi: 10.3390/cells11081364. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35456043 Free PMC article.
-
NADPH oxidase family proteins: signaling dynamics to disease management.Cell Mol Immunol. 2022 Jun;19(6):660-686. doi: 10.1038/s41423-022-00858-1. Epub 2022 May 18. Cell Mol Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35585127 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deficiency of LMP10 Attenuates Diet-Induced Atherosclerosis by Inhibiting Macrophage Polarization and Inflammation in Apolipoprotein E Deficient Mice.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Oct 23;8:592048. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.592048. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 33195259 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting protein modifications in metabolic diseases: molecular mechanisms and targeted therapies.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023 May 27;8(1):220. doi: 10.1038/s41392-023-01439-y. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023. PMID: 37244925 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Old blood from heterochronic parabionts accelerates vascular aging in young mice: transcriptomic signature of pathologic smooth muscle remodeling.Geroscience. 2022 Apr;44(2):953-981. doi: 10.1007/s11357-022-00519-1. Epub 2022 Feb 5. Geroscience. 2022. PMID: 35124764 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cardiovascular-diseases...
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

