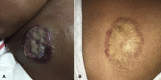
Propranolol-induced hyperkalemia in the management of infantile hemangioma
- PMID: 32258322
- PMCID: PMC7103665
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jdcr.2020.01.028
Propranolol-induced hyperkalemia in the management of infantile hemangioma
Keywords: atenolol; hemangioma; hyperkalemia; propranolol; β-blocker.
Figures
References
-
- Drolet B.A., Esterly N.B., Frieden I.J. Hemangiomas in children. N Engl J Med. 1999;34:173–181. - PubMed
-
- Léauté-Labrèze C., De la Roque E.D., Hubiche T. Propranolol for severe hemangiomas of infancy. N Engl J Med. 2008;358:2649–2651. - PubMed
-
- Fabre Pierre. Pierre Fabre obtains FDA approval to market Hemangeol for the treatment of infantile hemangioma. http://www.pierre-fabre.com/en/fda-approval-market-hemangeoltm Available at:
-
- Léaute-Labrèze C., Boccara O., Degrugillier-Chopinet C. Safety of oral propranolol for the treatment of infantile hemangioma: a systematic review. Pediatrics. 2016;138(4) e20160353. - PubMed
-
- Pavlakovic H., Kietz S., Lauerer P. Hyperkalemia complicating propranolol treatment of an infantile hemangioma. Pediatrics. 2010;126:e1589–e1593. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources