Differentially expressed mRNAs and lncRNAs shared between activated human hepatic stellate cells and nash fibrosis
- PMID: 32258441
- PMCID: PMC7109412
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrep.2020.100753
Differentially expressed mRNAs and lncRNAs shared between activated human hepatic stellate cells and nash fibrosis
Abstract
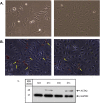
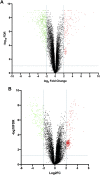
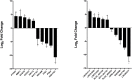
We previously reported dysregulated expression of liver-derived messenger RNA (mRNA) and long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) in patients with advanced fibrosis resulting from nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Here we sought to identify changes in mRNA and lncRNA levels associated with activation of hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), the predominant source of extracellular matrix production in the liver and key to NAFLD-related fibrogenesis. We performed expression profiling of mRNA and lncRNA from LX-2 cells, an immortalized human HSC cell line, treated to induce phenotypes resembling quiescent and myofibroblastic states. We identified 1964 mRNAs (1377 upregulated and 587 downregulated) and 1460 lncRNAs (665 upregulated and 795 downregulated) showing statistically significant evidence (FDR ≤0.05) for differential expression (fold change ≥|2|) between quiescent and activated states. Pathway analysis of differentially expressed genes showed enrichment for hepatic fibrosis (FDR = 1.35E-16), osteoarthritis (FDR = 1.47E-14), and axonal guidance signaling (FDR = 1.09E-09). We observed 127 lncRNAs/nearby mRNA pairs showing differential expression, the majority of which were dysregulated in the same direction. A comparison of differentially expressed transcripts in LX-2 cells with RNA-sequencing results from NAFLD patients with or without liver fibrosis revealed 1047 mRNAs and 91 lncRNAs shared between the two datasets, suggesting that some of the expression changes occurring during HSC activation can be observed in biopsied human tissue. These results identify lncRNA and mRNA expression patterns associated with activated human HSCs that appear to recapitulate human NAFLD fibrosis.
Keywords: Cirrhosis; Hepatic fibrosis; Hepatic stellate cells; Long noncoding RNA; Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
© 2020 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
CDS receives grant and consulting support from Ethicon Endo-Surgery. The remaining authors declare no competing financial and/or non-financial interests in relation to the work.
Figures
References
-
- Younossi Z., Tacke F., Arrese M., Chander Sharma B., Mostafa I., Bugianesi E. Global perspectives on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology. 2019;69(6):2672–2682. - PubMed
-
- Koek G.H., Liedorp P.R., Bast A. The role of oxidative stress in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Clin. Chim. Acta. 2011;412(15–16):1297–1305. - PubMed
-
- Jorge A.S., Andrade J.M., Paraiso A.F., Jorge G.C., Silveira C.M., de Souza L.R. Body mass index and the visceral adipose tissue expression of IL-6 and TNF-alpha are associated with the morphological severity of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in individuals with class III obesity. Obes. Res. Clin. Pract. 2018;12(Suppl 2):1–8. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

