Extraction of phytosterols and tocopherols from rapeseed oil waste by supercritical CO2 plus co-solvent: A comparison with conventional solvent extraction
- PMID: 32258458
- PMCID: PMC7103770
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e03592
Extraction of phytosterols and tocopherols from rapeseed oil waste by supercritical CO2 plus co-solvent: A comparison with conventional solvent extraction
Abstract
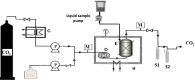
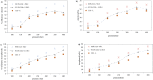
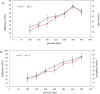
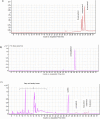
In the present study, modified extraction methods using supercritical CO2 were investigated in order to obtain high-added value compounds from rapeseed oil deodorizer distillate and comparisons were done with modified Soxhlet extraction (solvent extraction + silica). For supercritical fluid extraction (SFE), the optimal extraction parameters were temperature of 40 °C, pressure of 350 bar (for phytosterols), 400 bar (for tocopherol), 5 wt% ethanol as co-solvent, and saponification pretreatment. The optimized SFE procedure led to the recovery of three main phytosterols (50 wt % β-sitosterol, 23.91 wt % Brassicasterol, and 36.25 wt % Campesterol) and only α-tocopherol. Moreover, there was no synergistic effect with saponification pretreatment + co-solvent and the efficiency and concentration of target compounds were less than supercritical CO2 + co-solvent. Also, comparative Data showed that the efficiency of phytosterols and tocopherols was approximately three times higher (p < 0.05) in SFE relative to modified Soxhlet extraction. Furthermore, the use of ethanol (5 wt %) as co-solvent, improved phytosterols and tocopherol efficiency and purity. The SFE technique offers various advantages over the modified Soxhlet extraction technique, including increasing the solubility of tocopherols and sterols by using CO2+ co-solvent, minimized usage of toxic organic solvents and increased purity of extracted products.
Keywords: Food science; Food technology; Solvent extraction; Sterols; Supercritical fluid extraction; Tocopherol.
© 2020 The Authors.
Figures
References
-
- Sherazi S.T.H., Mahesar S.A. Vegetable oil deodorizer distillate: a dich, source of the natural bioactive components. J. Ole Sci. 2016;65:957–966. - PubMed
-
- Naz S., Sherazi S.T.H., Talpour F. Chemical Characterization of Canola and Sunfl ower oil deodorizer distillates. J. Food Nutr. Sci. 2014;17:115–120.
-
- Yang H., Yan F., Wu D., Huo M.J., Li Y. Cao, Recovery of phytosterols from waste residue of soybean oil deodorizer distillate. J. Bio Tech. 2010;101:1471–1476. - PubMed
-
- Cantrill R. 2008. Phytosterols, Phytostanols and Their Esters Chemical and Technical Assessment. 69th JECFA; pp. 1–13.
-
- Duba K.S., Fiori L. Supercritical CO2 extraction of grape seed oil: effect of process parameters on the extraction kinetics. J. Super Fluids. 2015;98:33–43.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

