Microemulsion-based approach for oral delivery of insulin: formulation design and characterization
- PMID: 32258491
- PMCID: PMC7113630
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e03650
Microemulsion-based approach for oral delivery of insulin: formulation design and characterization
Abstract
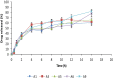
Oral delivery of insulin provides a good alternative because it is non-invasive and patient-friendly. However, multiple challenges affected this route. To overcome barriers for oral delivery of insulin, we aimed to develop a novel insulin-loaded microemulsion system based on snail mucin for oral administration. The strategy in the novel system of using mucin loading insulin into the inner core of prepared water in oil microemulsion to provide sustained released, increased in vivo stability and enhanced drug absorption in the gastrointestinal tract. We report how microemulsion composed of varying ratios of snail mucin and Tween® 80 (1:9-9:1) using oil/water emulsion preparation method influenced insulin performance after oral administration. The results obtained include an encapsulation efficiency of above 70 %; in vitro release was sustained over 10 h and in vivo evaluations in diabetic rat model shows that insulin-loaded microencapsulation effectively reduced blood glucose levels over a period >8 h after oral administration. Therefore, we suggest that the developed formulation for oral insulin can be a promising alternative dosage form for oral protein delivery.
Keywords: Biological sciences; Biotechnology; Diabetes; Materials application; Materials characterization; Microemulsions; Mucin; Oral-insulin; Pharmaceutical chemistry; Pharmacology; Tween® 80.
© 2020 Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures


References
-
- Abdallah M., Yuichi T., Hirofumi T. Design and evaluation of novel pH-sensitive chitosan nanoparticles fororal insulin delivery. Eur. J. Pharmaceut. Sci. 2011;42:445–451. - PubMed
-
- Adikwu M.U., Aneke K.O., Builders P.F. Biophysical properties of mucin and its use as a mucoadhesive agent in drug delivery: current development and future concepts. Niger. J. Pharmaceut. Res. 2005;4:60–69.
-
- Al-Salami H. Probiotics decreased the bioavailability of the bile acid analog, monoketocholic acid, when coadministered with gliclazide, in healthy but not diabetic rats. Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2012;37(2):99–108. - PubMed
-
- Amidi M.E., Mastrobattista W., Jiskoot W.E. Chitosan-baseddelivery systems for protein therapeutics and antigens. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2010;62:59–82. - PubMed
-
- Arhewoh M.I., Eraga S.O., Maroh O. Transdermal delivery of bovine serum albumin using snail mucin.East and central. Afr. J. Pharmaceut. 2014;17:18–24.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

