Human infection by Pasteurella canis - A case report
- PMID: 32258587
- PMCID: PMC6806975
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pbj.2017.01.005
Human infection by Pasteurella canis - A case report
Abstract
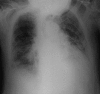
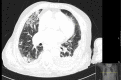
Pasteurella species are a component of the normal oropharyngeal flora in canine animals. In humans, the skin and soft tissue are the most common sites for Pasteurella infection and, less commonly, the respiratory tract can also be affected. We report a case of pneumonia by Pasteurella canis in a chronic respiratory disease patient with a history of permanent contact with a dog.
Keywords: Bacteremia; Pasteurella canis; Pneumonia.
Copyright 2017 PBJ-Associação Porto Biomedical/Porto Biomedical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Jorgenesen JH, Pfaller MA. 2015. Manual of clinical microbiology, 11th ed. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, DC.
-
- Casallas-Rivera M, Faccini-Martínez A, Perdomo-Beltrán N, Botero-García C, Bravo J, Pérez-Díaz C. Septicemia hemorrágica y empiema pleural por Pasteurella canis. Rev Chilena Infectol. 2016;33:85-88. - PubMed
-
- Albert TJ, Stevens DL. The first case of Pasteurella canis bacteremia: a cirrhotic patient with an open leg wound. Infection. 2010;38:483-485. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources