Cane Molasses Graphene Quantum Dots Passivated by PEG Functionalization for Detection of Metal Ions
- PMID: 32258911
- PMCID: PMC7114702
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.0c00098
Cane Molasses Graphene Quantum Dots Passivated by PEG Functionalization for Detection of Metal Ions
Abstract
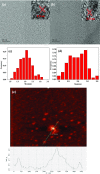
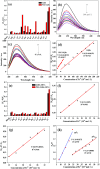
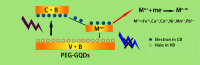
Poly(ethylene glycol) passivated graphene quantum dots (PEG-GQDs) were synthesized based on a green and effective strategy of the hydrothermal treatment of cane molasses. The prepared PEG-GQDs, with an average size of 2.5 nm, exhibit a brighter blue fluorescence and a higher quantum yield (QY) (up to approximately 21.32%) than the QY of GQDs without surface passivation (QY = 10.44%). The PEG-GQDs can be used to detect and quantify paramagnetic transition-metal ions including Fe3+, Cu2+, Co2+, Ni2+, Pb2+, and Mn2+. In the case of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) solution as a masking agent, Fe3+ ions can be well selectively determined in a transition-metal ion mixture, following the lowest limit of detection (LOD) of 5.77 μM. The quenching mechanism of Fe3+ on PEG-GQDs belongs to dynamic quenching. Furthermore, Fe3+ in human serum can be successfully detected by the PEG-GQDs, indicating that the green prepared PEG-GQDs can be applied as a promising candidate for the selective detection of Fe3+ in clinics.
Copyright © 2020 American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures



References
-
- Ju B.; Wang Y.; Zhang Y. M.; Zhang T.; Lu Z. H.; Li M. J.; Zhang S. X. A. Photostable and Low-Toxic Yellow-Green Carbon Dots for Highly Selective Detection of Explosive 2,4,6-Trinitrophenol Based on the Dual Electron Transfer Mechanism. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 13040–13047. 10.1021/acsami.8b02330. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Pan J. Q.; Sheng Y. Z.; Zhang J. X.; Wei J. M.; Huang P.; Zhang X.; Feng B. X. Preparation of carbon quantum dots/TiO2 nanotubes composites and their visible light catalytic applications. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 18082–18086. 10.1039/C4TA03528C. - DOI
-
- Wang L. P.; Wu X. Q.; Guo S. J.; Han M. M.; Zhou Y. J.; Sun Y.; Huang H.; Liu Y.; Kang Z. H. Mesoporous nitrogen, sulfur co-doped carbon dots/CoS hybrid as an efficient electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 2717–2723. 10.1039/C6TA09580A. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

