In Vitro to in Vivo Translation of Allosteric Modulator Concentration-Effect Relationships: Implications for Drug Discovery
- PMID: 32259076
- PMCID: PMC7088891
- DOI: 10.1021/acsptsci.9b00062
In Vitro to in Vivo Translation of Allosteric Modulator Concentration-Effect Relationships: Implications for Drug Discovery
Abstract
Allosteric modulation of GPCRs represents an increasingly explored approach in drug development. Due to complex pharmacology, however, the relationship(s) between modulator properties determined in vitro with in vivo concentration-effect phenomena is frequently unclear. We investigated key pharmacological properties of a set of metabotropic glutamate receptor 5 (mGlu5) positive allosteric modulators (PAMs) and their relevance to in vivo concentration-response relationships. These studies identified a significant relationship between in vitro PAM cooperativity (αβ), as well as the maximal response obtained from a simple in vitro PAM concentration-response experiment, with in vivo efficacy for reversal of amphetamine-induced hyperlocomotion. This correlation did not exist with PAM potency or affinity. Data across PAMs were then converged to calculate an in vivo concentration of glutamate putatively relevant to the mGlu5 PAM mechanism of action. This work demonstrates the ability to merge in vitro pharmacology profiles with relevant behavioral outcomes and also provides a novel method to estimate neurotransmitter concentrations in vivo.
Copyright © 2019 American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
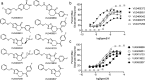




References
-
- Lindsley C. W.; Emmitte K. A.; Hopkins C. R.; Bridges T. M.; Gregory K. J.; Niswender C. M.; Conn P. J. (2016) Practical Strategies and Concepts in GPCR Allosteric Modulator Discovery: Recent Advances with Metabotropic Glutamate Receptors. Chem. Rev. 116, 6707–6741. 10.1021/acs.chemrev.5b00656. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
