Thyroid Hormone Enhances Neurite Outgrowth in Neuroscreen 1 Cells
- PMID: 32259096
- PMCID: PMC7111465
- DOI: 10.31531/2581-4745.1000104
Thyroid Hormone Enhances Neurite Outgrowth in Neuroscreen 1 Cells
Abstract
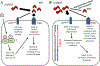
Objectives: Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disorder that affects millions of individuals. Moreover, hypothyroidism has been identified as one of the risk factors that may contribute to the development of AD. Here, we investigated whether there was a correlation among expression levels of proteins involved in the formation of AD lesions, neurite outgrowth, and thyroid hormone levels.
Methods: Cells were grown in media supplemented with different levels of 3,5,3'-triiodothyronine (T3) and then processed for neurite outgrowth and to prepare RNA samples. RNA samples were analysed using quantitative real-time PCR. Protein levels were measured using in cell-Western blotting analysis.
Results: By using neurite outgrowth studies, it was demonstrated that T3 treatment enhanced neurite outgrowth in NS-1 cells in a time- and dose-dependent manner. Quantitative real-time PCR studies further confirmed that NS-1 cells expressed substantial levels of TRα and significantly less TRβ, either of which could be responsible for the T3-dependent effects on neurite outgrowth. Although the overall tau protein expression was not affected in response to T3 treatment, the splicing of tau exon 10 was impacted in the direction of producing more tau molecules that excluded the exon (tau 3R).
Conclusion: The results of this study are critical not only to understand the probable link between hypothyroidism and AD but also in providing the basis for future prevention and treatment of AD in hypothyroid patients.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Amyloid precursor protein; Exon 10 splicing; NS-1 cell; Tau; Thyroid hormones.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest None declared.
Figures


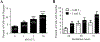


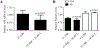
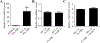

References
-
- Alzheimer’s Association. 2016 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimer’s Dement 2016; 12: 459–509. - PubMed
-
- Tozlu M, Cankurtaran M, Yavuz BB, et al. Functional Disability in Alzheimer Disease: A Validation Study of the Turkish Version of the Disability Assessment for Dementia Scale. J Geriat Psych Neurol 2014; 27: 237–246. - PubMed
-
- Takizawa C, Thompson PL, van Walsem A, et al. Epidemiological and economic burden of Alzheimer’s disease: a systematic literature review of data across Europe and the United States of America. J Alzheimers Dis 2015; 43: 1271–1284. - PubMed
-
- Hardy J, Selkoe DJ. The Amyloid Hypothesis of Alzheimer’s Disease: Progress and Problems on the Road to Therapeutics. Science 2002; 297: 353–356. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
