Cholesterol Stabilizes TAZ in Hepatocytes to Promote Experimental Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis
- PMID: 32259482
- PMCID: PMC7313619
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.03.010
Cholesterol Stabilizes TAZ in Hepatocytes to Promote Experimental Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis
Abstract
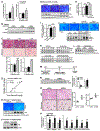
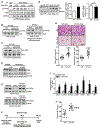
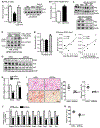
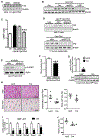
Incomplete understanding of how hepatosteatosis transitions to fibrotic non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) has limited therapeutic options. Two molecules that are elevated in hepatocytes in human NASH liver are cholesterol, whose mechanistic link to NASH remains incompletely understood, and TAZ, a transcriptional regulator that promotes fibrosis but whose mechanism of increase in NASH is unknown. We now show that increased hepatocyte cholesterol upregulates TAZ and promotes fibrotic NASH. ASTER-B/C-mediated internalization of plasma membrane cholesterol activates soluble adenylyl cyclase (sAC; ADCY10), triggering a calcium-RhoA-mediated pathway that suppresses β-TrCP/proteasome-mediated TAZ degradation. In mice fed with a cholesterol-rich NASH-inducing diet, hepatocyte-specific silencing of ASTER-B/C, sAC, or RhoA decreased TAZ and ameliorated fibrotic NASH. The cholesterol-TAZ pathway is present in primary human hepatocytes, and associations among liver cholesterol, TAZ, and RhoA in human NASH liver are consistent with the pathway. Thus, hepatocyte cholesterol contributes to fibrotic NASH by increasing TAZ, suggesting new targets for therapeutic intervention.
Keywords: ADCY10; Gramd1/ASTER; Hippo; NASH; RhoA; TAZ; WWTR1; cholesterol; liver fibrosis; sAC.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests J.B. and L.R.L. own equity interest in CEP Biotech, which has licensed commercialization of a panel of monoclonal antibodies directed against sAC. I.T. and X.W. are co-inventors of a patent application related to the topic of this study, and I.T. is a scientific consultant for Genevant, which is developing therapies for NASH.
Figures



Comment in
-
Liver cholesterol matters.Aging (Albany NY). 2020 Oct 26;12(20):19828-19829. doi: 10.18632/aging.104208. Epub 2020 Oct 26. Aging (Albany NY). 2020. PMID: 33125343 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Adams D, Gonzalez-Duarte A, O’Riordan WD, Yang CC, Ueda M, Kristen AV, Tournev I, Schmidt HH, Coelho T, Berk JL, et al. (2018). Patisiran, an RNAi therapeutic, for hereditary transthyretin amyloidosis. N Engl J Med 379, 11–21. - PubMed
-
- Angulo P, Kleiner DE, Dam-Larsen S, Adams LA, Bjornsson ES, Charatcharoenwitthaya P, Mills PR, Keach JC, Lafferty HD, Stahler A, et al. (2015a). Liver fibrosis, but no other histologic features, is associated with long-term outcomes of patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology 149, 389–397 e310. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Angulo P, Machado MV, and Diehl AM (2015b). Fibrosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: mechanisms and clinical implications. Semin Liver Dis 35, 132–145. - PubMed
-
- Athyros VG, Alexandrides TK, Bilianou H, Cholongitas E, Doumas M, Ganotakis ES, Goudevenos J, Elisaf MS, Germanidis G, Giouleme O, et al. (2017). The use of statins alone, or in combination with pioglitazone and other drugs, for the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease/non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and related cardiovascular risk. An Expert Panel Statement. Metabolism 71, 17–32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P01 HL020948/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R00 DK115778/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HD088571/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R35 CA196878/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007343/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK116620/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL087123/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH110550/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DE015964/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG061290/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL132412/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL136618/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK103818/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL146358/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN276201200017C/LM/NLM NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA013696/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK119767/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K99 DK115778/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL067773/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

