Phospho-proteomic discovery of novel signal transducers including thioredoxin-interacting protein as mediators of erythropoietin-dependent human erythropoiesis
- PMID: 32259549
- PMCID: PMC7480993
- DOI: 10.1016/j.exphem.2020.03.003
Phospho-proteomic discovery of novel signal transducers including thioredoxin-interacting protein as mediators of erythropoietin-dependent human erythropoiesis
Abstract
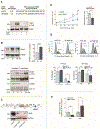
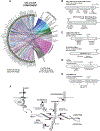
Erythroid cell formation critically depends on signals transduced via erythropoietin (EPO)/EPO receptor (EPOR)/JAK2 complexes. This includes not only core response modules (e.g., JAK2/STAT5, RAS/MEK/ERK), but also specialized effectors (e.g., erythroferrone, ASCT2 glutamine transport, Spi2A). By using phospho-proteomics and a human erythroblastic cell model, we identify 121 new EPO target proteins, together with their EPO-modulated domains and phosphosites. Gene ontology (GO) enrichment for "Molecular Function" identified adaptor proteins as one top EPO target category. This includes a novel EPOR/JAK2-coupled network of actin assemblage modifiers, with adaptors DLG-1, DLG-3, WAS, WASL, and CD2AP as prime components. "Cellular Component" GO analysis further identified 19 new EPO-modulated cytoskeletal targets including the erythroid cytoskeletal targets spectrin A, spectrin B, adducin 2, and glycophorin C. In each, EPO-induced phosphorylation occurred at pY sites and subdomains, which suggests coordinated regulation by EPO of the erythroid cytoskeleton. GO analysis of "Biological Processes" further revealed metabolic regulators as a likewise unexpected EPO target set. Targets included aldolase A, pyruvate dehydrogenase α1, and thioredoxin-interacting protein (TXNIP), with EPO-modulated p-Y sites in each occurring within functional subdomains. In TXNIP, EPO-induced phosphorylation occurred at novel p-T349 and p-S358 sites, and was paralleled by rapid increases in TXNIP levels. In UT7epo-E and primary human stem cell (HSC)-derived erythroid progenitor cells, lentivirus-mediated short hairpin RNA knockdown studies revealed novel pro-erythropoietic roles for TXNIP. Specifically, TXNIP's knockdown sharply inhibited c-KIT expression; compromised EPO dose-dependent erythroblast proliferation and survival; and delayed late-stage erythroblast formation. Overall, new insight is provided into EPO's diverse action mechanisms and TXNIP's contributions to EPO-dependent human erythropoiesis.
Copyright © 2020 ISEH -- Society for Hematology and Stem Cells. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest disclosure The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Phospho-PTM proteomic discovery of novel EPO- modulated kinases and phosphatases, including PTPN18 as a positive regulator of EPOR/JAK2 Signaling.Cell Signal. 2020 May;69:109554. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2020.109554. Epub 2020 Feb 3. Cell Signal. 2020. PMID: 32027948 Free PMC article.
-
RHEX, a novel regulator of human erythroid progenitor cell expansion and erythroblast development.J Exp Med. 2014 Aug 25;211(9):1715-22. doi: 10.1084/jem.20130624. Epub 2014 Aug 4. J Exp Med. 2014. PMID: 25092874 Free PMC article.
-
Lnk inhibits erythropoiesis and Epo-dependent JAK2 activation and downstream signaling pathways.Blood. 2005 Jun 15;105(12):4604-12. doi: 10.1182/blood-2004-10-4093. Epub 2005 Feb 10. Blood. 2005. PMID: 15705783 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging EPO and EPO receptor regulators and signal transducers.Blood. 2015 Jun 4;125(23):3536-41. doi: 10.1182/blood-2014-11-575357. Epub 2015 Apr 17. Blood. 2015. PMID: 25887776 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting EPO and EPO receptor pathways in anemia and dysregulated erythropoiesis.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2016;20(3):287-301. doi: 10.1517/14728222.2016.1090975. Epub 2015 Sep 30. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2016. PMID: 26419263 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Integrative proteomics reveals principles of dynamic phosphosignaling networks in human erythropoiesis.Mol Syst Biol. 2020 Dec;16(12):e9813. doi: 10.15252/msb.20209813. Mol Syst Biol. 2020. PMID: 33259127 Free PMC article.
-
STAT5 as a Key Protein of Erythropoietin Signalization.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 1;22(13):7109. doi: 10.3390/ijms22137109. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34281163 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differentially Expressed Genes Induced by Erythropoietin Receptor Overexpression in Rat Mammary Adenocarcinoma RAMA 37-28 Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 9;24(10):8482. doi: 10.3390/ijms24108482. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37239828 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment and streamlined preparation of low-cytotoxicity lentiviral vectors for mobilized human hematopoietic stem cell transduction.Exp Hematol. 2020 Jun;86:28-42.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.exphem.2020.05.009. Epub 2020 May 27. Exp Hematol. 2020. PMID: 32473295 Free PMC article.
-
The Emerging Role of TXNIP in Ischemic and Cardiovascular Diseases; A Novel Marker and Therapeutic Target.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Feb 8;22(4):1693. doi: 10.3390/ijms22041693. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33567593 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Wu H, Liu X, Jaenisch R, Lodish HF. Generation of committed erythroid BFU-E and CFU-E progenitors does not require erythropoietin or the erythropoietin receptor. Cell. 1995;83(1):59–67. - PubMed
-
- Stauder R, Valent P, Theurl I. Anemia at older age: etiologies, clinical implications, and management. Blood. 2018;131(5):505–514. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

