Deletion of Mouse Setd4 Promotes the Recovery of Hematopoietic Failure
- PMID: 32259569
- PMCID: PMC7321877
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2020.03.026
Deletion of Mouse Setd4 Promotes the Recovery of Hematopoietic Failure
Abstract
Purpose: Acquired hematopoietic failure is commonly caused by therapeutic and accidental exposure of the bone marrow (BM) to toxic agents. Efficient recovery from BM failure is dictated not only by the intrinsic sensitivity and proliferation capacity of the hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells but also by the BM environment niche. Identification of genetic factors that improve recovery from hematopoietic failure is essential. Vertebrate SETD4 is a poorly characterized and putatively nonhistone methyltransferase. This study aims to identify the roles of SETD4 in BM recovery.
Methods and materials: An inducible SETD4 knockout mouse model (Setd4flox/flox;Rosa26-CreERT2+) was used. Adult sex-matched littermates were treated with tamoxifen to induce Setd4 deletion or oil as the control. Tamoxifen-treated Setd4wt/wt;Rosa26-CreERT2+ mice were included as another control. Those mice were irradiated to induce hematopoietic syndrome and analyzed to identify the roles and mechanisms of Setd4 in of BM recovery.
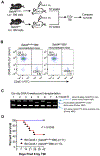
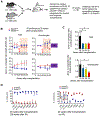
Results: Loss of Setd4 in adult mice improved the survival of whole-body irradiation-induced BM failure. This was associated with improved recoveries of long-term and short-term hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) and early progenitor cells. BM transplantation analyses surprisingly showed that the improved recovery was not due to radiation resistance of the Setd4-deficient HSCs but that Setd4-deficient HSCs were actually more sensitive to radiation. However, the Setd4-deficient mice were better recipients for allogeneic HSC transplantation. Furthermore, there was enhanced splenic erythropoiesis in Setd4-deficient mice.
Conclusion: These findings not only revealed a previously unrecognized role of Setd4 as a unique modulator of hematopoiesis but also underscored the critical role of the BM niche in recovery from hematopoietic failure. Our study also implicated Setd4 as a potential target for therapeutic inhibition to improve the conditioning of the BM niche before allogeneic transplantation.
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
Unmasking the mammalian SET domain-containing protein 4.NAR Cancer. 2022 Jul 13;4(3):zcac021. doi: 10.1093/narcan/zcac021. eCollection 2022 Sep. NAR Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35854936 Free PMC article.
-
Adiponectin Enhances Quiescence Exit of Murine Hematopoietic Stem Cells and Hematopoietic Recovery Through mTORC1 Potentiation.Stem Cells. 2017 Jul;35(7):1835-1848. doi: 10.1002/stem.2640. Epub 2017 May 23. Stem Cells. 2017. PMID: 28480607
-
Loss of Setd4 delays radiation-induced thymic lymphoma in mice.DNA Repair (Amst). 2020 Feb;86:102754. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2019.102754. Epub 2019 Nov 25. DNA Repair (Amst). 2020. PMID: 31794893 Free PMC article.
-
Extravascular coagulation in hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell regulation.Blood. 2018 Jul 12;132(2):123-131. doi: 10.1182/blood-2017-12-768986. Epub 2018 Jun 4. Blood. 2018. PMID: 29866813 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting the Hematopoietic Stem Cell Niche in β-Thalassemia and Sickle Cell Disease.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 May 11;15(5):592. doi: 10.3390/ph15050592. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35631417 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
SETD4-mediated KU70 methylation suppresses apoptosis.Cell Rep. 2022 May 10;39(6):110794. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2022.110794. Cell Rep. 2022. PMID: 35545041 Free PMC article.
-
The mammalian Ku70 C-terminus SAP domain is required to repair DNA damage.Nucleic Acids Res. 2025 Jun 6;53(11):gkaf499. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaf499. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025. PMID: 40498075 Free PMC article.
-
Somatic Functional Deletions of Upstream Open Reading Frame-Associated Initiation and Termination Codons in Human Cancer.Biomedicines. 2021 May 29;9(6):618. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9060618. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34072580 Free PMC article.
-
Unmasking the mammalian SET domain-containing protein 4.NAR Cancer. 2022 Jul 13;4(3):zcac021. doi: 10.1093/narcan/zcac021. eCollection 2022 Sep. NAR Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35854936 Free PMC article.
-
SETD4 in the Proliferation, Migration, Angiogenesis, Myogenic Differentiation and Genomic Methylation of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2021 Aug;17(4):1374-1389. doi: 10.1007/s12015-021-10121-1. Epub 2021 Jan 27. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2021. PMID: 33506343
References
-
- Pronk E, Raaijmakers MH. The mesenchymal niche in mds. Blood 2019;133:1031–1038. - PubMed
-
- Sieff CA. Introduction to acquired and inherited bone marrow failure. Hematology/Oncology Clinics 2018;32:569–580. - PubMed
-
- Bogliolo M, Surralles J. Fanconi anemia: A model disease for studies on human genetics and advanced therapeutics. Current opinion in genetics & development 2015;33:32–40. - PubMed
-
- Shimoni A, Nagler A. Radioimmunotherapy and stem-cell transplantation in the treatment of aggressive b-cell lymphoma. Leukemia & lymphoma 2007;48:2110–2120. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

