DNA vaccines: prime time is now
- PMID: 32259744
- PMCID: PMC7195337
- DOI: 10.1016/j.coi.2020.01.006
DNA vaccines: prime time is now
Abstract
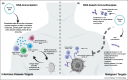
Recently newer synthetic DNA vaccines have been rapidly advanced to clinical study and have demonstrated an impressive degree of immune potency and tolerability. Improvements in DNA delivery over prior needle and syringe approaches include jet delivery, gene gun delivery, among others. Among the most effective of these new delivery methods, advanced electroporation (EP), combined with other advances, induces robust humoral and cellular immunity in both preventative as well as therapeutic studies. Advancements in the design of the DNA inserts include leader sequence changes, RNA and codon optimizations, improved insert designs, increased concentrations of DNA, and skin delivery, appear to complement newer delivery strategies. These advances also provide a framework for the in vivo production of synthetic DNA biologics. In this review, we focus on recent studies of synthetic DNA vaccines in the clinic for the prevention or treatment of infectious diseases with a focus on adaptive electroporation for delivery, and briefly summarize novel preclinical data advancing the in vivo delivery of DNA-encoded antibody-like biologics.
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Jorritsma S., Gowans E., Grubor-Bauk B., Wijesundara D. Delivery methods to increase cellular uptake and immunogenicity of DNA vaccines. Vaccine. 2016;34:5488–5494. - PubMed
-
- Khan A.S., Broderick K.E., Sardesai N.Y. Electroporation Protocols. Springer; 2014. Clinical development of intramuscular electroporation: providing a “boost” for DNA vaccines; pp. 279–289. - PubMed
-
- Lambricht L., Lopes A., Kos S., Sersa G., Préat V., Vandermeulen G. Clinical potential of electroporation for gene therapy and DNA vaccine delivery. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2016;13:295–310. - PubMed
-
- Chattergoon M.A., Robinson T.M., Boyer J.D., Weiner D.B. Specific immune induction following DNA-based immunization through in vivo transfection and activation of macrophages/antigen-presenting cells. J Immunol. 1998;160:5707–5718. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

