Pituitary Function after High-Dose 177Lu-DOTATATE Therapy and Long-Term Follow-Up
- PMID: 32259830
- PMCID: PMC8117394
- DOI: 10.1159/000507761
Pituitary Function after High-Dose 177Lu-DOTATATE Therapy and Long-Term Follow-Up
Abstract
Introduction: The pituitary gland has a high expression of somatostatin receptors and is therefore a potential organ at risk for radiation-induced toxicity after 177Lu-DOTATATE treatment.
Objective: To study changes in pituitary function in patients with neuroendocrine tumors (NETs) treated with dosimetry-based 177Lu-DOTATATE to detect possible late toxicity.
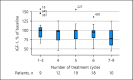
Methods: 68 patients from a phase II clinical trial of dosimetry-based, individualized 177Lu-DOTATATE therapy were included in this analysis. Patients had received a median of 5 (range 3-9) treatment cycles of 7.4 GBq/cycle. Median follow-up was 30 months (range 11-89). The GH/IGF-1 axis, gonadotropins, and adrenal and thyroid axes were analyzed at baseline and on a yearly basis thereafter. Percent changes in hormonal levels over time were analyzed statistically using a linear mixed model and described graphically using box plots. The absorbed radiation dose to the pituitary was estimated based on post-therapeutic imaging, and the results analyzed versus percent change in IGF-1 levels over time.
Results: A statistically significant decrease in IGF-1 levels was found (p < 0.005), which correlated with the number of treatment cycles (p = 0.008) and the absorbed radiation dose (p = 0.03). A similar decrease, although non-significant, was seen in gonadotropins in postmenopausal women, while in men there was an increase during the first years after therapy, after which the levels returned to baseline. No change was observed in the adrenal or thyroid axes.
Conclusions: No signs of severe endocrine disorders were detected, although a significant decrease in the GH/IGF-1 axis was found, where dosimetric analyses indicated radiation-induced damage to the pituitary gland as a probable cause.
Keywords: 177Lu-DOTATATE; Neuroendocrine tumor; Peptide receptor radionuclide therapy; Pituitary; Radiotherapy.
© 2020 The Author(s) Published by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
Anna Sundlöv has acted as a consultant/lecturer/advisory board member for Ipsen, Novartis, Sam Nordic, and Spago Nanomedical. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures



References
-
- Kim SJ, Pak K, Koo PJ, Kwak JJ, Chang S. The efficacy of (177)Lu-labelled peptide receptor radionuclide therapy in patients with neuroendocrine tumours: a meta-analysis. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2015 Dec;42((13)):1964–70. - PubMed
-
- Garske-Román U, Sandström M, Fröss Baron K, Lundin L, Hellman P, Welin S, et al. Prospective observational study of 177Lu-DOTA-octreotate therapy in 200 patients with advanced metastasized neuroendocrine tumours (NETs): feasibility and impact of a dosimetry-guided study protocol on outcome and toxicity. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2018 Jun;45((6)):970–88. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Reubi JC. Peptide receptor expression in GEP-NET. Virchows Arch. 2007 Aug;451((S1 Suppl 1)):S47–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

