Immune Responses and Protective Efficacy of a Formalin-Killed Francisella Noatunensis Subsp. Orientalis Vaccine Evaluated through Intraperitoneal and Immersion Challenge Methods in Oreochromis Niloticus
- PMID: 32260212
- PMCID: PMC7348880
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines8020163
Immune Responses and Protective Efficacy of a Formalin-Killed Francisella Noatunensis Subsp. Orientalis Vaccine Evaluated through Intraperitoneal and Immersion Challenge Methods in Oreochromis Niloticus
Abstract
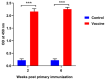
Francisella noatunensis subsp. orientalis (Fno), an intracellular bacterium, causes systemic granulomatous diseases, resulting in high mortality and huge economic losses in Taiwanese tilapia farming. In this study, we tested the efficacy of a formalin-killed Fno vaccine in cultured tilapia. Fno was isolated from diseased tilapia, inactivated with formalin, and mixed with the mineral oil base adjuvant (MontanideTM ISA 763 AVG). A total of 300 tilapia were divided into two groups. The experimental group was intraperitoneally injected with 0.1 mL of vaccine, which was substituted with phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) in the control group. A booster was administered at 2 weeks post-immunization. Tilapia were challenged at 6 weeks post primary immunization by intraperitoneal (IP) injection and immersion methods. Mortality was recorded at 21 and 60 days. The results revealed that the vaccine induced a greater antibody titer and led to 71% and 76% of relative percent survival (RPS) after the IP and immersion challenge. The transcripts of proinflammatory cytokines and immune-related genes, including interleukin-1β (IL-1β), tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFα), C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 8 (CXCL8), and interleukin-17C (IL-17C), were significantly upregulated after vaccination. Additionally, vaccinated fish had lower bacterial loads in the blood and lower granuloma intensities in the kidney, spleen, liver, and gill than control fish. The results in this study demonstrate that the inactivated Fno vaccine could be an essential resource in Taiwanese tilapia farming.
Keywords: Francisella noatunensis susbsp. orientalis; Oreochromis niloticus; formalin-killed vaccine; immune response.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be constructed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Chern R.S., Chao C.B. Outbreaks of a Disease Caused by Rickettsia-like Organism in Cultured Tilapias in Taiwan. Fish Pathol. 1994;29:61–71. doi: 10.3147/jsfp.29.61. - DOI
-
- Hsieh C.Y., Tung M.C., Tu C., Chang C.D., Tsai S.S. Enzootics of visceral granulomas associated with Francisella-like organism infection in tilapia (Oreochromis spp.) Aquaculture. 2006;254:129–138. doi: 10.1016/j.aquaculture.2006.03.044. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

