Inflammation and Premature Ageing in Chronic Kidney Disease
- PMID: 32260373
- PMCID: PMC7232447
- DOI: 10.3390/toxins12040227
Inflammation and Premature Ageing in Chronic Kidney Disease
Abstract
Persistent low-grade inflammation and premature ageing are hallmarks of the uremic phenotype and contribute to impaired health status, reduced quality of life, and premature mortality in chronic kidney disease (CKD). Because there is a huge global burden of disease due to CKD, treatment strategies targeting inflammation and premature ageing in CKD are of particular interest. Several distinct features of the uremic phenotype may represent potential treatment options to attenuate the risk of progression and poor outcome in CKD. The nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (NRF2)-kelch-like erythroid cell-derived protein with CNC homology [ECH]-associated protein 1 (KEAP1) signaling pathway, the endocrine phosphate-fibroblast growth factor-23-klotho axis, increased cellular senescence, and impaired mitochondrial biogenesis are currently the most promising candidates, and different pharmaceutical compounds are already under evaluation. If studies in humans show beneficial effects, carefully phenotyped patients with CKD can benefit from them.
Keywords: ageing; chronic kidney disease; end-stage kidney disease; inflammation; premature ageing; senescence; uremic toxins.
Conflict of interest statement
Peter Stenvinkel serves on scientific advisory boards of Baxter, Reata, and Astra Zeneca. The other authors of this manuscript have nothing to declare.
Figures

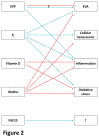
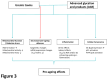
References
-
- Bikbov B., Purcell C.A., Levey A.S., Smith M., Abdoli A., Abebe M., Adebayo O.M., Afarideh M., Agarwal S.K., Agudelo-Botero M., et al. Global, regional, and national burden of chronic kidney disease, 1990–2017: A systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study 2017. Lancet. 2020;395:709–733. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30045-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ridker P.M., MacFadyen J.G., Glynn R.J., Koenig W., Libby P., Everett B.M., Lefkowitz M., Thuren T., Cornel J.H. Inhibition of interleukin-1β by canakinumab and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with chronic kidney disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018;71:2405–2414. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2018.03.490. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- Novo Nordisk postdoctoral fellowship run in partnership with Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden/Novo Nordisk/International
- 20180571 and 20160384/Swedish Heart and Lung Foundation/International
- N/A/King Gustaf V and Queen Victoria Freemason Foundation/International
- N/A/Professor Nanna Svartz Foundation/International
- 20170365/Stockholms Läns Landsting/International
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

