High-density lipoproteins during sepsis: from bench to bedside
- PMID: 32264946
- PMCID: PMC7140566
- DOI: 10.1186/s13054-020-02860-3
High-density lipoproteins during sepsis: from bench to bedside
Abstract
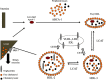
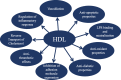
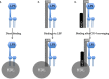
High-density lipoproteins (HDLs) represent a family of particle characterized by the presence of apolipoprotein A-I (apoA-I) and by their ability to transport cholesterol from peripheral tissues back to the liver conferring them a cardioprotective function. HDLs also display pleiotropic properties including antioxidant, anti-apoptotic, anti-thrombotic, anti-inflammatory, or anti-infectious functions. Clinical data demonstrate that HDL cholesterol levels decrease rapidly during sepsis and that these low levels are correlated with morbi-mortality. Experimental studies emphasized notable structural and functional modifications of HDL particles in inflammatory states, including sepsis. Finally, HDL infusion in animal models of sepsis improved survival and provided a global endothelial protective effect. These clinical and experimental studies reinforce the potential of HDL therapy in human sepsis. In this review, we will detail the different effects of HDLs that may be relevant under inflammatory conditions and the lipoprotein changes during sepsis and we will discuss the potentiality of HDL therapy in sepsis.
Keywords: Endothelium; High-density lipoprotein (HDL); Inflammation; Intensive care unit (ICU); Lipopolysaccharide (LPS); Sepsis; Sepsis therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Angus DC, van der Poll T. Severe sepsis and septic shock. N Engl J Med. 2013;369(21):2063. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous