Ocular manifestations of a hospitalised patient with confirmed 2019 novel coronavirus disease
- PMID: 32265202
- PMCID: PMC7211077
- DOI: 10.1136/bjophthalmol-2020-316304
Ocular manifestations of a hospitalised patient with confirmed 2019 novel coronavirus disease
Abstract
Purpose: To report the ocular characteristics and the presence of viral RNA of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) in conjunctival swab specimens in a patient with confirmed 2019 novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19).
Participant and methods: A 30-year-old man with confirmed COVID-19 and bilateral acute conjunctivitis which occurred 13 days after illness onset. Based on detailed ophthalmic examination, reverse transcription PCR (RT-PCR) was performed to detect SARS-CoV-2 virus in conjunctival swabs. The ocular characteristics, presence of viral RNA and viral dynamics of SARS-CoV-2 in the conjunctival specimens were evaluated.
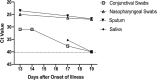
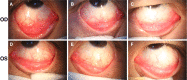
Results: Slit lamp examination showed bilateral acute follicular conjunctivitis. RT-PCR assay demonstrated the presence of viral RNA in conjunctival specimen 13 days after onset (cycle threshold value: 31). The conjunctival swab specimens remained positive for SARS-CoV-2 on 14 and 17 days after onset. On day 19, RT-PCR result was negative for SARS-CoV-2.
Conclusion: SARS-CoV-2 is capable of causing ocular complications such as viral conjunctivitis in the middle phase of illness. Precautionary measures are recommended when examining infected patients throughout the clinical course of the infection. However, conjunctival sampling might not be useful for early diagnosis because the virus may not appear initially in the conjunctiva.
Keywords: conjunctiva; infection.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2020. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures


Comment in
-
Not the 2020 we asked for.Br J Ophthalmol. 2020 Jun;104(6):741. doi: 10.1136/bjophthalmol-2020-316403. Epub 2020 Apr 10. Br J Ophthalmol. 2020. PMID: 32277012 No abstract available.
References
-
- World Health Organization Novel coronavirus (COVID-19) situation, 2020. Available: https://experience.arcgis.com/experience/685d0ace521648f8a5beeeee1b9125cd
-
- Wang Y, Detrick B, Yu ZX, et al. The role of apoptosis within the retina of coronavirus-infected mice. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2000;41:3011–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
