Current status of cell-based therapies for respiratory virus infections: applicability to COVID-19
- PMID: 32265310
- PMCID: PMC7144273
- DOI: 10.1183/13993003.00858-2020
Current status of cell-based therapies for respiratory virus infections: applicability to COVID-19
Abstract
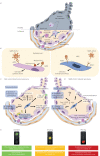
The severe respiratory consequences of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic have prompted urgent need for novel therapies. Cell-based approaches, primarily using mesenchymal stem (stromal) cells (MSCs), have demonstrated safety and possible efficacy in patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS), although they are not yet well studied in respiratory virus-induced ARDS. Limited pre-clinical data suggest that systemic MSC administration can significantly reduce respiratory virus (influenza strains H5N1 and H9N2)-induced lung injury; however, there are no available data in models of coronavirus respiratory infection.There is a rapidly increasing number of clinical investigations of cell-based therapy approaches for COVID-19. These utilise a range of different cell sources, doses, dosing strategies and targeted patient populations. To provide a rational strategy to maximise potential therapeutic use, it is critically important to understand the relevant pre-clinical studies and postulated mechanisms of MSC actions in respiratory virus-induced lung injuries. This review presents these, along with consideration of current clinical investigations.
Copyright ©ERS 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: M. Khoury reports grants from CONICYT (FONDEF 2016, IT16I10084), during the conduct of the study; stipend received from Cells for Cells, outside the submitted work; has patents WO2014135924A1 pending, WO2017064670A2 pending, WO2017064672A1 pending and WO/2019/051623 pending; and is CSO of Cells for Cells, a University spin-off developing therapies for osteoarthritis, pulpitis and cardiac failure, and Regenero, a consortium for Chilean regenerative medicine (public and private funding), for skin ulcer and Lupus. Conflict of interest: J. Cuenca reports grants from CONICYT (FONDEF 2016, IT16I10084), during the conduct of the study; stipend received from Cells for Cells, outside the submitted work; and is a research scientist for Cells for Cells, a University spin-off developing therapies for osteoarthritis, pulpitis and cardiac failure, and Regenero, a consortium for Chilean regenerative medicine (public and private funding), for skin ulcer and Lupus. Conflict of interest: F.F. Cruz has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: F.E. Figueroa has a patent WO/2019/051623 pending and is a board member of Cells for Cells, as the director of the programme of translational cell therapy at Universidad de los Andes, the academic institution that originated the Consorcio Corfo Regenero and the Cells for Cells biotechnological spin-off. Conflict of interest: P.R.M. Rocco has nothing to disclose. Conflict of interest: D.J. Weiss reports grants from NIH, Cystic Fibrosis Foundation and US Department of Defense, outside the submitted work.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
