The Impacts of Herbal Medicines and Natural Products on Regulating the Hepatic Lipid Metabolism
- PMID: 32265720
- PMCID: PMC7105674
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00351
The Impacts of Herbal Medicines and Natural Products on Regulating the Hepatic Lipid Metabolism
Abstract
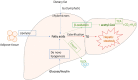
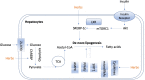
The dysregulation of hepatic lipid metabolism is one of the hallmarks in many liver diseases including alcoholic liver diseases (ALD) and non-alcoholic fatty liver diseases (NAFLD). Hepatic inflammation, lipoperoxidative stress as well as the imbalance between lipid availability and lipid disposal, are direct causes of liver steatosis. The application of herbal medicines with anti-oxidative stress and lipid-balancing properties has been extensively attempted as pharmaceutical intervention for liver disorders in experimental and clinical studies. Although the molecular mechanisms underlying their hepatoprotective effects warrant further exploration, increasing evidence demonstrated that many herbal medicines are involved in regulating lipid accumulation processes including hepatic lipolytic and lipogenic pathways, such as mitochondrial and peroxisomal β-oxidation, the secretion of very low density lipoprotein (VLDL), the non-esterified fatty acid (NEFA) uptake, and some vital hepatic lipogenic enzymes. Therefore, in this review, the pathways or crucial mediators participated in the dysregulation of hepatic lipid metabolism are systematically summarized, followed by the current evidences and advances in the positive impacts of herbal medicines and natural products on the lipid metabolism pathways are detailed. Furthermore, several herbal formulas, herbs or herbal derivatives, such as Erchen Dection, Danshen, resveratrol, and berberine, which have been extensively studied for their promising potential in mediating lipid metabolism, are particularly highlighted in this review.
Keywords: fatty liver; herbal medicines; lipid metabolism; lipogenesis; lipolysis; natural products.
Copyright © 2020 Li, Xu, Guo, Chen, Zhang, Tan, Wang and Feng.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Recent insights into hepatic lipid metabolism in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).Prog Lipid Res. 2009 Jan;48(1):1-26. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2008.08.001. Epub 2008 Sep 9. Prog Lipid Res. 2009. PMID: 18824034 Review.
-
Hepatic lipid accumulation: cause and consequence of dysregulated glucoregulatory hormones.J Endocrinol. 2017 Jul;234(1):R1-R21. doi: 10.1530/JOE-16-0513. Epub 2017 Apr 20. J Endocrinol. 2017. PMID: 28428362 Review.
-
Chinese herbal medicines: The modulator of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease targeting oxidative stress.J Ethnopharmacol. 2024 Jan 10;318(Pt B):116927. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.116927. Epub 2023 Jul 31. J Ethnopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 37532073 Review.
-
The promising roles of medicinal plants and bioactive compounds on hepatic lipid metabolism in the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in animal models: molecular targets.Arch Physiol Biochem. 2023 Dec;129(6):1262-1278. doi: 10.1080/13813455.2021.1939387. Epub 2021 Jun 21. Arch Physiol Biochem. 2023. PMID: 34153200 Review.
-
Herbal medicines for the prevention of alcoholic liver disease: a review.J Ethnopharmacol. 2012 Dec 18;144(3):457-65. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2012.09.044. Epub 2012 Oct 9. J Ethnopharmacol. 2012. PMID: 23058988 Review.
Cited by
-
Apple pomace and rosemary extract ameliorates hepatic steatosis in fructose-fed rats: Association with enhancing fatty acid oxidation and suppressing inflammation.Exp Ther Med. 2020 Sep;20(3):1975-1986. doi: 10.3892/etm.2020.8910. Epub 2020 Jun 19. Exp Ther Med. 2020. PMID: 32782507 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Therapeutic Implication of Herbal Medicine in Mitochondria-Mediated Oxidative Stress-Related Liver Diseases.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Oct 17;11(10):2041. doi: 10.3390/antiox11102041. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36290765 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Isoschaftoside Reverses Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease via Activating Autophagy In Vivo and In Vitro.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Jun 27;2022:2122563. doi: 10.1155/2022/2122563. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 35795282 Free PMC article.
-
Berberine ameliorates nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by decreasing the liver lipid content via reversing the abnormal expression of MTTP and LDLR.Exp Ther Med. 2021 Oct;22(4):1109. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.10543. Epub 2021 Aug 3. Exp Ther Med. 2021. PMID: 34504563 Free PMC article.
-
Puerarin Modulates Hepatic Farnesoid X Receptor and Gut Microbiota in High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 12;25(10):5274. doi: 10.3390/ijms25105274. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38791314 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arablou T., Aryaeian N., Valizadeh M., Sharifi F., Hosseini A., Djalali M. (2014). The effect of ginger consumption on glycemic status, lipid profile and some inflammatory markers in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Int. J. Food Sci. Nutr. 65 (4), 515–520. 10.3109/09637486.2014.880671 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources