Functional Results of Arthroscopic Treatment in Patients With Femoroacetabular and Subspine Impingement Diagnosed With a 3-Dimensional Dynamic Study
- PMID: 32266357
- PMCID: PMC7120805
- DOI: 10.1016/j.asmr.2019.10.007
Functional Results of Arthroscopic Treatment in Patients With Femoroacetabular and Subspine Impingement Diagnosed With a 3-Dimensional Dynamic Study
Abstract
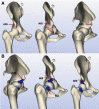
Purpose: To describe the functional results of arthroscopic treatment in patients with femoroacetabular impingement (FAI) and subspine impingement (SSI) evaluated with a 3-dimensional (3D) dynamic study.
Methods: This was a retrospective observational study of patients with a diagnosis of FAI and SSI, evaluated with a 3D dynamic computed tomography scan with Move Forward software, who underwent hip arthroscopy between February 2015 and December 2017. Measurements of the alpha angle, femoral anteversion, acetabular anteversion, lateral center-edge angle, and Tönnis angle were extracted from the 3D dynamic study. Functionality was evaluated using the Western Ontario McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index before and 12 months after surgery.
Results: We analyzed 22 hips in 17 patients (9 female and 8 male patients) with an average age of 34.6 ± 14.3 years. Of the 22 hips, 15 had cam morphology, 6 had mixed morphology, and 1 had pincer morphology. Of the hips, 11 had a type I spine, 10 had type II, and 1 had type III. The average alpha angle, Tönnis angle, femoral anteversion, and acetabular anteversion were 61.9° ± 11.1°, 2.5° ± 6.4°, 8.8° ± 6.8°, and 15.1° ± 7.1°, respectively. The median lateral center-edge angle was 38.1° (interquartile range, 32.6°-43.5°). At 1-year follow-up, a decrease in the Western Ontario McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index score (P = .001) and an increase in the flexion angle (P < .001) were observed. No cases needed posterior surgical revision because of persistent pain.
Conclusions: Arthroscopic treatment provides symptom relief and good functional results in patients with FAI and SSI.
Level of evidence: Level IV, therapeutic case series.
© 2019 by the Arthroscopy Association of North America. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Ganz R., Parvizi J., Beck M., Leunig M., Notzli H., Siebenrock K.A. Femoroacetabular impingement: A cause for osteoarthritis of the hip. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2003;417:112–120. - PubMed
-
- Hetsroni I., Larson C.M., Dela Torre K., Zbeda R.M., Magennis E., Kelly B.T. Anterior inferior iliac spine deformity as an extra-articular source for hip impingement: A series of 10 patients treated with arthroscopic decompression. Arthroscopy. 2012;28:1644–1653. - PubMed
-
- Aguilera-Bohorquez B., Brugiatti M., Coaquira R., Cantor E. Frequency of subspine impingement in patients with femoroacetabular impingement evaluated with a 3-dimensional dynamic study. Arthroscopy. 2019;35:91–96. - PubMed
-
- Samim M., Walter W., Gyftopoulos S., Poultsides L., Youm T. MRI assessment of subspine impingement: Features beyond the anterior inferior iliac spine morphology. Radiology. 2019;293:412–421. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

