In-silico homology assisted identification of inhibitor of RNA binding against 2019-nCoV N-protein (N terminal domain)
- PMID: 32266867
- PMCID: PMC7256351
- DOI: 10.1080/07391102.2020.1753580
In-silico homology assisted identification of inhibitor of RNA binding against 2019-nCoV N-protein (N terminal domain)
Abstract
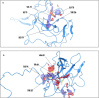
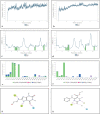
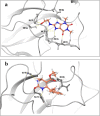
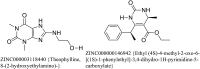
The N terminal domain (NTD) of Nucleocapsid protein (N protein) of coronavirus (CoV) binds to the viral (+) sense RNA and results in CoV ribonucleoprotien (CoV RNP) complex, essential for the virus replication. In this study, the RNA-binding N terminal domain (NTD) of the N protein was targeted for the identification of possible inhibitors of RNA binding. Two NTD structures of N proteins were selected (2OFZ and 1SSK, 92% homology) for virtual screening of 56,079 compounds from Asinex and Maybridge library to identify top 15 hits for each of the targets based on 'docking score'. These top-hits were further screened for MM-GBSA binding free energy, pharmacokinetic properties (QikProp) and drug-likeness (SwissADME) and subjected to molecular dynamics (MD) studies. Two suitable binders (ZINC00003118440 and ZINC0000146942) against the target 2OFZ were identified. ZINC00003118440 is a theophylline derivative under the drug class 'bronchodilators' and further screening with approved bronchodilators was also studied to identify their ability to bind to the RNA binding region on the N protein. The other identified top hit is ZINC0000146942, which is a 3,4dihydropyrimidone class molecule. Hence this study suggests two important class of compounds, theophylline and pyrimidone derivaties as possible inhibitors of RNA binding to the N terminal domain of N protein of coronavirus, thus opening new avenues for in vitro validations. Communicated by Ramaswamy H. Sarma.
Keywords: 2019 novel corona virus; 2019-nCoV; N terminal domain; Nucleocapsid protein; RNA binding; SARS-CoV-2; drug design.
Figures

References
-
- Adasme-Carreño F., Muñoz-Gutierrez C., Caballero J., & Alzate-Morales J. H. (2014). Performance of the MM/GBSA scoring using a binding site hydrogen bond network-based frame selection: The protein kinase case. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 16(27), 14047–14058. doi:10.1039/C4CP01378F - DOI - PubMed
-
- Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19)—Events as they happen. (n.d.). Retrieved March 16, 2020, from https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/events-a...
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
