Diagnosing peripheral neuropathy in South-East Asia: A focus on diabetic neuropathy
- PMID: 32268012
- PMCID: PMC7477502
- DOI: 10.1111/jdi.13269
Diagnosing peripheral neuropathy in South-East Asia: A focus on diabetic neuropathy
Abstract
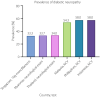
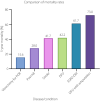
Burning and stabbing pain in the feet and lower limbs can have a significant impact on the activities of daily living, including walking, climbing stairs and sleeping. Peripheral neuropathy in particular is often misdiagnosed or underdiagnosed because of a lack of awareness amongst both patients and physicians. Furthermore, crude screening tools, such as the 10-g monofilament, only detect advanced neuropathy and a normal test will lead to false reassurance of those with small fiber mediated painful neuropathy. The underestimation of peripheral neuropathy is highly prevalent in the South-East Asia region due to a lack of consensus guidance on routine screening and diagnostic pathways. Although neuropathy as a result of diabetes is the most common cause in the region, other causes due to infections (human immunodeficiency virus, hepatitis B or C virus), chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy, drug-induced neuropathy (cancer chemotherapy, antiretrovirals and antituberculous drugs) and vitamin deficiencies (vitamin B1 , B6 , B12 , D) should be actively excluded.
Keywords: Diagnosis; Peripheral neuropathy; South-East Asia.
© 2020 The Authors. Journal of Diabetes Investigation published by Asian Association for the Study of Diabetes (AASD) and John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Lotan I, Hellman MA, Steiner I. Diagnostic criteria of chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy in diabetes mellitus. Acta Neurol Scand 2015; 132: 278–283. - PubMed
-
- Karami‐Mohajeri S, Nikfar S, Abdollahi M. A systematic review on the nerve‐muscle electrophysiology in human organophosphorus pesticide exposure. Hum Exp Toxicol 2014; 33: 92–102. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

