Neonatal Resuscitation and Postresuscitation Care of Infants Born to Mothers with Suspected or Confirmed SARS-CoV-2 Infection
- PMID: 32268381
- PMCID: PMC7356083
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0040-1709688
Neonatal Resuscitation and Postresuscitation Care of Infants Born to Mothers with Suspected or Confirmed SARS-CoV-2 Infection
Abstract
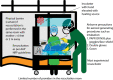
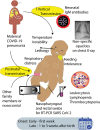
The first case of novel coronavirus disease of 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) was reported in November2019. The rapid progression to a global pandemic of COVID-19 has had profound medical, social, and economic consequences. Pregnant women and newborns represent a vulnerable population. However, the precise impact of this novel virus on the fetus and neonate remains uncertain. Appropriate protection of health care workers and newly born infants during and after delivery by a COVID-19 mother is essential. There is some disagreement among expert organizations on an optimal approach based on resource availability, surge volume, and potential risk of transmission. The manuscript outlines the precautions and steps to be taken before, during, and after resuscitation of a newborn born to a COVID-19 mother, including three optional variations of current standards involving shared-decision making with parents for perinatal management, resuscitation of the newborn, disposition, nutrition, and postdischarge care. The availability of resources may also drive the application of these guidelines. More evidence and research are needed to assess the risk of vertical and horizontal transmission of SARS-CoV-2 and its impact on fetal and neonatal outcomes. KEY POINTS: · The risk of vertical transmission is unclear; transmission from family members/providers to neonates is possible.. · Optimal personal-protective-equipment (airborne vs. droplet/contact precautions) for providers is crucial to prevent transmission.. · Parents should be engaged in shared decision-making with options for rooming in, skin-to-skin contact, and breastfeeding..
Thieme Medical Publishers 333 Seventh Avenue, New York, NY 10001, USA.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures


References
-
- World Health Organization. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Situation Report-74. Updated March 20, 2020. Available at:https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/situation-reports/2.... Accessed April 6, 2020
-
- The Gurdian. First Covid-19 case happened in November, China government records show - report. Available at:https://www.theguardian.com/world/2020/mar/13/first-covid-19-case-happen.... Accessed April 2, 2020
-
- –Peristats. United States. Quick Facts: Population. Available at:https://www.marchofdimes.org/Peristats/ViewTopic.aspx?reg=99&top=14&lev=.... Accessed April 2, 2020

