Kidney tissue hypoxia dictates T cell-mediated injury in murine lupus nephritis
- PMID: 32269165
- PMCID: PMC8055156
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aay1620
Kidney tissue hypoxia dictates T cell-mediated injury in murine lupus nephritis
Abstract
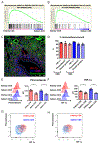
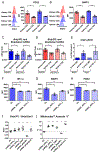
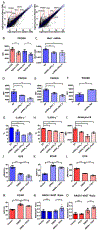
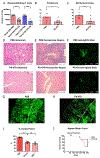
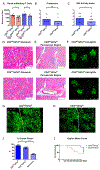
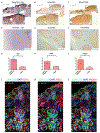
The kidney is a frequent target of autoimmune injury, including in systemic lupus erythematosus; however, how immune cells adapt to kidney's unique environment and contribute to tissue damage is unknown. We found that renal tissue, which normally has low oxygen tension, becomes more hypoxic in lupus nephritis. In the injured mouse tissue, renal-infiltrating CD4+ and CD8+ T cells express hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1), which alters their cellular metabolism and prevents their apoptosis in hypoxia. HIF-1-dependent gene-regulated pathways were also up-regulated in renal-infiltrating T cells in human lupus nephritis. Perturbation of these environmental adaptations by selective HIF-1 blockade inhibited infiltrating T cells and reversed tissue hypoxia and injury in murine models of lupus. The results suggest that targeting HIF-1 might be effective for treating renal injury in autoimmune diseases.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: J.C. received research funding from AbbVie which was used to partially support this work.
Figures
Comment in
-
HIF1α blockade reduces kidney injury in lupus nephritis.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2020 Jun;16(6):295. doi: 10.1038/s41584-020-0430-4. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2020. PMID: 32376996 No abstract available.
-
The role of hypoxia in the pathogenesis of lupus nephritis.Kidney Int. 2020 Oct;98(4):821-823. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2020.06.008. Epub 2020 Jun 26. Kidney Int. 2020. PMID: 32599087 No abstract available.
References
-
- Deng W, Ren Y, Feng X, Yao G, Chen W, Sun Y, Wang H, Gao X, Sun L, Hypoxia inducible factor-1 alpha promotes mesangial cell proliferation in lupus nephritis. American journal of nephrology 40, 507–515 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Clever D, Roychoudhuri R, Constantinides MG, Askenase MH, Sukumar M, Klebanoff CA, Eil RL, Hickman HD, Yu Z, Pan JH, Palmer DC, Phan AT, Goulding J, Gattinoni L, Goldrath AW, Belkaid Y, Restifo NP, Oxygen Sensing by T Cells Establishes an Immunologically Tolerant Metastatic Niche. Cell 166, 1117–1131.e1114 (2016). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Whitehouse T, Stotz M, Taylor V, Stidwill R, Singer M, Tissue oxygen and hemodynamics in renal medulla, cortex, and corticomedullary junction during hemorrhage-reperfusion. American journal of physiology. Renal physiology 291, F647–653 (2006). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

