ENL initiates multivalent phase separation of the super elongation complex (SEC) in controlling rapid transcriptional activation
- PMID: 32270036
- PMCID: PMC7112754
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.aay4858
ENL initiates multivalent phase separation of the super elongation complex (SEC) in controlling rapid transcriptional activation
Abstract
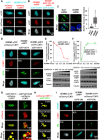
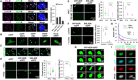
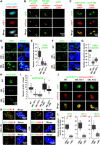
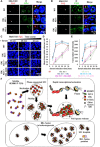
Release of paused RNA polymerase II (Pol II) requires incorporation of the positive transcription elongation factor b (P-TEFb) into the super elongation complex (SEC), thus resulting in rapid yet synchronous transcriptional activation. However, the mechanism underlying dynamic transition of P-TEFb from inactive to active state remains unclear. Here, we found that the SEC components are able to compartmentalize and concentrate P-TEFb via liquid-liquid phase separation from the soluble inactive HEXIM1 containing the P-TEFb complex. Specifically, ENL or its intrinsically disordered region is sufficient to initiate the liquid droplet formation of SEC. AFF4 functions together with ENL in fluidizing SEC droplets. SEC droplets are fast and dynamically formed upon serum exposure and required for rapid transcriptional induction. We also found that the fusion of ENL with MLL can boost SEC phase separation. In summary, our results suggest a critical role of multivalent phase separation of SEC in controlling transcriptional pause release.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works. Distributed under a Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License 4.0 (CC BY-NC).
Figures


References
-
- Luo Z., Lin C., Shilatifard A., The super elongation complex (SEC) family in transcriptional control. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 13, 543–547 (2012). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

