RETRACTED: Molecular targeting of FATP4 transporter for oral delivery of therapeutic peptide
- PMID: 32270048
- PMCID: PMC7112756
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.aba0145
RETRACTED: Molecular targeting of FATP4 transporter for oral delivery of therapeutic peptide
Retraction in
-
Retraction of the Research Article: "Molecular targeting of FATP4 transporter for oral delivery of therapeutic peptide" by Z. Hu, S. Nizzero, S. Goel, L. E. Hinkle, X. Wu, C. Li, M. Ferrari and H. Shen.Sci Adv. 2020 Jun 26;6(26):eabc9572. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abc9752. eCollection 2020 Jun. Sci Adv. 2020. PMID: 32637628 Free PMC article.
Abstract
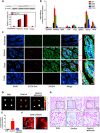
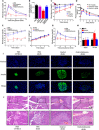
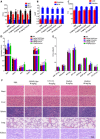
Low oral bioavailability of peptide drugs has limited their application to parenteral administration, which suffers from poor patient compliance. Here, we show that molecular targeting of the FATP4 transporter is an effective approach to specifically transport long-chain fatty acid (LCFA)-conjugated peptides across the enterocytic membrane and, thus, enables oral delivery of drug peptides. We packaged LCFA-conjugated exendin-4 (LCFA-Ex4) into liposomes and coated with chitosan nanoparticles to form an orally deliverable Ex4 (OraEx4). OraEx4 protected LCFA-Ex4 from damage by the gastric fluid and released LCFA-Ex4 in the intestinal cavity, where LCFA-Ex4 was transported across the enterocyte membrane by the FAPT4 transporter. OraEx4 had a high bioavailability of 24.8% with respect to subcutaneous injection and exhibited a substantial hypoglycemic effect in murine models of diabetes mellitus. Thus, molecular targeting of the FATP4 transporter enhances oral absorption of therapeutic peptides and provides a platform for oral peptide drug development.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works. Distributed under a Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License 4.0 (CC BY-NC).
Figures


References
-
- Moroz E., Matoori S., Leroux J.-C., Oral delivery of macromolecular drugs: Where we are after almost 100years of attempts. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 101, 108–121 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Goldberg M., Gomez-Orellana I., Challenges for the oral delivery of macromolecules. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2, 289–295 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Menzel C., Holzeisen T., Laffleur F., Zaichik S., Abdulkarim M., Gumbleton M., Bernkop-Schnürch A., In vivo evaluation of an oral self-emulsifying drug delivery system (SEDDS) for exenatide. J. Control. Release 277, 165–172 (2018). - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

