Major depressive disorder and cardiometabolic diseases: a bidirectional Mendelian randomisation study
- PMID: 32270255
- PMCID: PMC7286869
- DOI: 10.1007/s00125-020-05131-6
Major depressive disorder and cardiometabolic diseases: a bidirectional Mendelian randomisation study
Abstract
Aims/hypothesis: Observational studies have shown a bidirectional association between major depressive disorder (MDD) and cardiometabolic diseases. We conducted a two-sample bidirectional Mendelian randomisation (MR) study to assess the causal associations of MDD with type 2 diabetes, coronary artery disease (CAD) and heart failure and vice versa.
Methods: We extracted summary-level data for MDD, type 2 diabetes, CAD and heart failure from corresponding published large genome-wide association studies of individuals mainly of European-descent. In total, 96 SNPs for MDD, 202 SNPs for type 2 diabetes, 44 SNPs for CAD and 12 SNPs for heart failure were proposed as instrumental variables at the genome-wide significance level (p < 5 × 10-8). The random-effects inverse-variance weighted method was used for the main analyses.
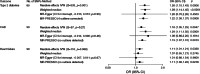
Results: Genetic liability to MDD was significantly associated with type 2 diabetes and CAD at the Bonferroni-corrected significance level. The ORs of type 2 diabetes and CAD were respectively 1.26 (95% CI 1.10, 1.43; p = 6 × 10-4) and 1.16 (95% CI 1.05, 1.29; p = 0.0047) per one-unit increase in loge odds of MDD. There was a suggestive association between MDD and heart failure (OR 1.11 [95% CI 1.01, 1.21]; p = 0.033). We found limited evidence supporting causal effects of cardiometabolic diseases on MDD risk in the reverse MR analyses.
Conclusions/interpretation: The present study strengthened the evidence that MDD is a potential risk factor for type 2 diabetes and CAD. Whether MDD is causally related to heart failure needs further study.
Data availability: All data included in this study were uploaded as supplements and are also publicly available through published GWASs and open GWAS datasets (UK Biobank, 23andMe and Psychiatric Genomics: https://datashare.is.ed.ac.uk/handle/10283/3203; DIAGRAM: http://diagram-consortium.org/downloads.html; CARDIoGRAMplusCD4: www.cardiogramplusc4d.org/; HERMES: http://www.kp4cd.org/datasets/mi). Graphical abstract.
Keywords: Coronary artery disease; Heart failure; Major depression disorder; Mendelian randomisation analysis; Type 2 diabetes.
Figures


References
-
- World Health Organization . Depression and other common mental disorders: global health estimates. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2017.
-
- Carnethon MR, Kinder LS, Fair JM, Stafford RS, Fortmann SP. Symptoms of depression as a risk factor for incident diabetes: findings from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Epidemiologic Follow-up Study, 1971–1992. Am J Epidemiol. 2003;158(5):416–423. doi: 10.1093/aje/kwg172. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

