Small G protein signaling modulator 3 (SGSM3) knockdown attenuates apoptosis and cardiogenic differentiation in rat mesenchymal stem cells exposed to hypoxia
- PMID: 32271805
- PMCID: PMC7145021
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0231272
Small G protein signaling modulator 3 (SGSM3) knockdown attenuates apoptosis and cardiogenic differentiation in rat mesenchymal stem cells exposed to hypoxia
Abstract
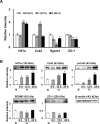
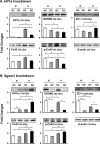
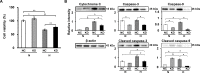
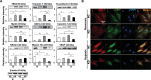
Connexin 43 (Cx43) may be important in cell death and survival due to cell-to-cell communication-independent mechanisms. In our previous study, we found that small G protein signaling modulator 3 (SGSM3), a partner of Cx43, contributes to myocardial infarction (MI) in rat hearts. Based on these previous results, we hypothesized that SGSM3 could also play a role in bone marrow-derived rat mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), which differentiate into cardiomyocytes and/or cells with comparable phenotypes under low oxygen conditions. Cx43 and Cx43-related factor expression profiles were compared between normoxic and hypoxic conditions according to exposure time, and Sgsm3 gene knockdown (KD) using siRNA transfection was performed to validate the interaction between SGSM3 and Cx43 and to determine the roles of SGSM3 in rat MSCs. We identified that SGSM3 interacts with Cx43 in MSCs under different oxygen conditions and that Sgsm3 knockdown inhibits apoptosis and cardiomyocyte differentiation under hypoxic stress. SGSM3/Sgsm3 probably has an effect on MSC survival and thus therapeutic potential in diseased hearts, but SGSM3 may worsen the development of MSC-based therapeutic approaches in regenerative medicine. This study was performed to help us better understand the mechanisms involved in the therapeutic efficacy of MSCs, as well as provide data that could be used pharmacologically.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Interaction of small G protein signaling modulator 3 with connexin 43 contributes to myocardial infarction in rat hearts.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017 Sep 16;491(2):429-435. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.07.081. Epub 2017 Jul 14. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017. PMID: 28716730
-
Protective effects of kenpaullone on cardiomyocytes following H2O2-induced oxidative stress are attributed to inhibition of connexin 43 degradation by SGSM3.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018 May 5;499(2):368-373. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.03.166. Epub 2018 Mar 26. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018. PMID: 29577900
-
Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells transport connexin43 via tunneling nanotubes to alleviate isopreterenol-induced myocardial hypertrophy.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025 May 6;16(1):229. doi: 10.1186/s13287-025-04339-w. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2025. PMID: 40329337 Free PMC article.
-
Pre-treatment of mesenchymal stem cells with a combination of growth factors enhances gap junction formation, cytoprotective effect on cardiomyocytes, and therapeutic efficacy for myocardial infarction.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008 Mar 4;51(9):933-43. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2007.11.040. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2008. PMID: 18308163 Clinical Trial.
-
The effect of macrophage-cardiomyocyte interactions on cardiovascular diseases and development of potential drugs.Mol Biol Rep. 2024 Oct 17;51(1):1056. doi: 10.1007/s11033-024-09944-1. Mol Biol Rep. 2024. PMID: 39417949 Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanotransduction in Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) Differentiation: A Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Apr 21;23(9):4580. doi: 10.3390/ijms23094580. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35562971 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Systematic Compilation of Human SH3 Domains: A Versatile Superfamily in Cellular Signaling.Cells. 2023 Aug 12;12(16):2054. doi: 10.3390/cells12162054. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37626864 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanotransduction of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) during cardiomyocytes differentiation.Heliyon. 2022 Nov 14;8(11):e11624. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e11624. eCollection 2022 Nov. Heliyon. 2022. PMID: 36425431 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

