Grading and management of cytokine release syndrome in patients treated with tisagenlecleucel in the JULIET trial
- PMID: 32271899
- PMCID: PMC7160283
- DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2019001304
Grading and management of cytokine release syndrome in patients treated with tisagenlecleucel in the JULIET trial
Abstract
Chimeric antigen receptor T-cell (CAR-T) therapy yields durable responses in patients with relapsed/refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (r/r DLBCL). Cytokine release syndrome (CRS) is a CAR-T therapy-related adverse event. To date, clinical trials of different CAR-T products have not been aligned on CRS grading scales and management algorithms. We assessed concordance between the Penn, Lee, and American Society for Transplantation and Cellular Therapy (ASTCT) grading systems by retrospectively regrading CRS events in the JULIET (A Phase 2, Single Arm, Multicenter Trial to Determine the Efficacy and Safety of CTL019 in Adult Patients With Relapsed or Refractory DLBCL) trial. Four medical experts with experience treating patients with 3 different CAR-T products independently regraded individual patient-level CRS events from the phase 2, global, pivotal JULIET trial (#NCT02445248). As of 8 December 2017, a total of 111 patients with r/r DLBCL underwent infusion with tisagenlecleucel. Sixty-four patients had CRS events graded per the Penn scale; on retrospective review, 63 and 61 patients had CRS events regraded per the Lee and ASTCT criteria, respectively. The Lee scale yielded concordance for 39, lower grade for 20, and higher grade for 5 events compared with the Penn scale. The ASTCT criteria provided concordance for 37, lower grade for 23, and higher grade for 4 events compared with the Penn scale. Sixteen (14%) of 111 patients in the JULIET trial received tocilizumab, all for severe events (Penn grade 3/4 CRS). This study is the first to assess concordance between 3 CRS grading scales using the same patient data set and to compare tocilizumab use according to the Lee scale in the JULIET trial and the ZUMA-1 (Long-Term Safety and Activity of Axicabtagene Ciloleucel in Refractory Large B-Cell Lymphoma) trial. This analysis describes key differences between grading scales and may inform CRS management practices.
© 2020 by The American Society of Hematology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: S.J.S. reports consultancy, honoraria, membership on an entity’s Board of Directors or advisory committees, and research funding from Celgene; consultancy and honoraria from Dava Oncology; honoraria and research funding from Genentech; membership on an entity’s Board of Directors or advisory committees for Gilead and Pfizer; consultancy, honoraria, and research funding from Merck; honoraria, membership on an entity’s Board of Directors or advisory committees, and research funding from Novartis; consultancy, honoraria, and membership on an entity’s Board of Directors or advisory committees from Nordic Nanovector; and honoraria from OncLive and Physicians’ Education Source, LLC. R.T.M. reports honoraria, membership on an entity’s Board of Directors or advisory committees, and research funding from Novartis; consultancy and honoraria from CRSPR Therapeutics, Incyte, and Juno Therapeutics; honoraria from Kite Therapeutics; patents and royalties from Athersys, Inc.; and employment by Oregon Health & Science University. R.T.M. also provided consultant services to and received payment from Novartis; this potential conflict of interest has been reviewed and managed by Oregon Health & Science University. E.S.R. is employed by Novartis. J.L. and J.E.S. are employed by the Analysis Group, Inc., which received funding from Novartis. V.V.R. is employed by Novartis. F.L.L. is a scientific advisor for Kite Pharma and Novartis; and reports consultancy for the Cellular BioMedicine Group Inc. D.G.M. receives research funding from Kite Pharma, a Gilead Company, and Celgene; receives research funding from and has patents licensed or pending with Juno Therapeutics, a Celgene/Bristol-Myers Squibb company; has participated in advisory board and/or protocol-specific data monitoring committee meetings for BioLine RX, Kite Pharma, Gilead, Genentech, Novartis, Juno Therapeutics, and Celgene and received honoraria; and is a member of the A2 Biotherapeutics Scientific Advisory Board and has stock options.
Figures
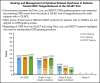
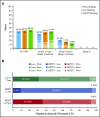
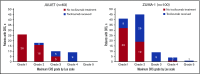
References
-
- Schuster SJ, Bishop MR, Tam C, et al. Sustained disease control for adult patients with relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: an updated analysis of JULIET, a global pivotal phase 2 trial of tisagenlecleucel [abstract]. Blood. 2018;132(suppl 1). Abstract 1684.
-
- Schuster SJ, Bishop MR, Tam CS, et al. ; JULIET Investigators . Tisagenlecleucel in adult relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. N Engl J Med. 2019;380(1):45-56. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

