Vitamin A Absorption Determined in Rats Using a Plasma Isotope Ratio Method
- PMID: 32271921
- PMCID: PMC7330459
- DOI: 10.1093/jn/nxaa092
Vitamin A Absorption Determined in Rats Using a Plasma Isotope Ratio Method
Abstract
Background: Better methods are needed for determining vitamin A absorption efficiency.
Objective: Our objective was to measure vitamin A absorption in rats by adapting a plasma isotope ratio method previously used to determine cholesterol absorption.
Methods: Male Sprague-Dawley rats [n = 14; 340 ± 16 g (mean ± SD)] received an oral tracer dose of [3H]retinyl acetate in oil plus an intravenous dose of [14C]vitamin A-labeled lymph prepared in a donor rat that had received [14C]retinyl acetate intraduodenally. Blood samples were collected on days 1, 2, 3, 6, 9, and 12, and plasma was analyzed for 3H and 14C; vitamin A absorption was calculated for each sample as (fraction of oral dose/fraction of intravenous dose) × 100. Radioactivity was also measured in feces and urine collected as pools on days 3, 6, 9, and 12 and in liver and remaining carcass on day 12.
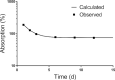
Results: Vitamin A absorption calculated as the plasma isotope ratio was >100% on day 1, 78% ± 5% on day 6, 76% ± 5% on day 9, and 74% ± 5% on day 12; fitting the data to an exponential function plus a constant predicted an absorption of 75% by day 14. Recovery of the oral dose in feces (day 0 to day 6) was low (6.2% ± 0.84%, n = 10) and the mean isotope ratio in day 9-12 urine pool was lower than that in plasma.
Conclusions: The plasma isotope ratio holds promise for estimating vitamin A absorption, but additional work is needed to determine how long studies need to be and if the doses should be administered simultaneously. For application of this method in humans, artificial chylomicrons labeled with a stable isotope of retinyl acetate could be used for the intravenous dose, with a different isotope required for the oral dose.
Keywords: isotope ratio method; isotopes; rats; vitamin A; vitamin A absorption.
Copyright © The Author(s) on behalf of the American Society for Nutrition 2020.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Use of model-based compartmental analysis to study effects of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin on vitamin A kinetics in rats.Toxicol Sci. 1998 Jul;44(1):1-13. doi: 10.1006/toxs.1998.2467. Toxicol Sci. 1998. PMID: 9720135
-
Validation of a dual-isotope plasma ratio method for measurement of cholesterol absorption in rats.J Lipid Res. 1974 Sep;15(5):465-73. J Lipid Res. 1974. PMID: 4472423
-
Dual isotope test for assessing beta-carotene cleavage to vitamin A in humans.Eur J Nutr. 2002 Aug;41(4):141-7. doi: 10.1007/s00394-002-0368-0. Eur J Nutr. 2002. PMID: 12242581
-
Determination of cholesterol absorption in humans: from radiolabel to stable isotope studies.Isotopes Environ Health Stud. 2003 Dec;39(4):247-57. doi: 10.1080/10256010310001621155. Isotopes Environ Health Stud. 2003. PMID: 14711170 Review.
-
Fractional cholesterol absorption measurements in humans: determinants of the blood-based dual stable isotope tracer technique.J Clin Lipidol. 2015 Jan-Feb;9(1):14-25. doi: 10.1016/j.jacl.2014.11.002. Epub 2014 Nov 13. J Clin Lipidol. 2015. PMID: 25670356 Review.
Cited by
-
Vitamin A Absorption Efficiency Determined by Compartmental Analysis of Postprandial Plasma Retinyl Ester Kinetics in Theoretical Humans.J Nutr. 2020 Aug 1;150(8):2223-2229. doi: 10.1093/jn/nxaa176. J Nutr. 2020. PMID: 32614427 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blomhoff R, Green MH, Green JB, Berg T, Norum KR. Vitamin A metabolism: new perspectives on absorption, transport and storage. Physiol Rev. 1991;71:951–90. - PubMed
-
- International Atomic Energy Agency/Harvest-Plus/US Agency for International Development. Analysis of stable isotope data to estimate vitamin A body stores. Vienna: International Atomic Energy Agency; 2008.
-
- Allen LE, Green MH, Green JB. Correspondence re: S.E. Dew et al., Effects of pharmacological retinoids on several vitamin A-metabolizing enzymes. Cancer Res. 1994;54:3319–20. - PubMed
-
- Sivakumar B, Reddy V. Absorption of labelled vitamin A in children during infection. Br J Nutr. 1972;27:299–304. - PubMed

