Signal of Carotid Intraplaque Hemorrhage on MR T1-Weighted Imaging: Association with Acute Cerebral Infarct
- PMID: 32273265
- PMCID: PMC7228181
- DOI: 10.3174/ajnr.A6498
Signal of Carotid Intraplaque Hemorrhage on MR T1-Weighted Imaging: Association with Acute Cerebral Infarct
Abstract
Background and purpose: Identifying the mere presence of carotid intraplaque hemorrhage would be insufficient to accurately discriminate the presence of acute cerebral infarct. We aimed to investigate the association between signal intensity ratios of carotid intraplaque hemorrhage on T1-weighted MR imaging and acute cerebral infarct in patients with hemorrhagic carotid plaques using MR vessel wall imaging.
Materials and methods: Symptomatic patients with carotid intraplaque hemorrhage were included. The signal intensity ratios of carotid intraplaque hemorrhage against muscle on T1-weighted, TOF, and MPRAGE images were measured. The acute cerebral infarct was determined on the hemisphere ipsilateral to the carotid intraplaque hemorrhage. The association between signal intensity ratios of carotid intraplaque hemorrhage and acute cerebral infarct was analyzed.
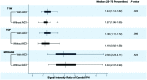
Results: Of 109 included patients (mean, 66.8 ± 9.9 years of age; 96 men), 40 (36.7%) had acute cerebral infarct. Patients with acute cerebral infarct had significantly higher signal intensity ratios of carotid intraplaque hemorrhage on T1-weighted images than those without (Median, 1.44; 25-75 Percentiles, 1.14-1.82 versus Median, 1.27; 25-75 Percentiles, 1.06-1.55, P = .022). Logistic regression analysis revealed that the signal intensity ratio of carotid intraplaque hemorrhage on T1-weighted images was significantly associated with acute cerebral infarct before (OR, 4.08; 95% CI, 1.34-12.40; P = .013) and after (OR, 3.34; 95% CI, 1.08-10.31; P = .036) adjustment for clinical confounding factors. However, this association was not significant when further adjusted for occlusion of the carotid artery (P = .058) and volumes of intraplaque hemorrhage and lipid-rich necrotic core (P = .458).
Conclusions: The signal intensity ratio of carotid intraplaque hemorrhage on T1-weighted images is associated with acute cerebral infarct in symptomatic patients with carotid hemorrhagic plaques. This association is independent of traditional risk factors but not of the size of plaque composition. The possibility of applying T1 signals of carotid intraplaque hemorrhage to predict subsequent cerebrovascular ischemic events needs to be prospectively verified.
© 2020 by American Journal of Neuroradiology.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Ipsilateral plaques display higher T1 signals than contralateral plaques in recently symptomatic patients with bilateral carotid intraplaque hemorrhage.Atherosclerosis. 2017 Feb;257:78-85. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2017.01.001. Epub 2017 Jan 12. Atherosclerosis. 2017. PMID: 28110259 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid Core Burden Index Assessed by Near-Infrared Spectroscopy of Symptomatic Carotid Plaques: Association with Magnetic Resonance T1-Weighted Imaging.Cerebrovasc Dis. 2021;50(5):597-604. doi: 10.1159/000516888. Epub 2021 Jun 18. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2021. PMID: 34148038
-
The potential role of IDEAL MRI for identification of lipids and hemorrhage in carotid artery plaques.Magn Reson Imaging. 2018 Jun;49:25-31. doi: 10.1016/j.mri.2017.12.002. Epub 2017 Dec 5. Magn Reson Imaging. 2018. PMID: 29217492
-
Contemporary carotid imaging: from degree of stenosis to plaque vulnerability.J Neurosurg. 2016 Jan;124(1):27-42. doi: 10.3171/2015.1.JNS142452. Epub 2015 Jul 31. J Neurosurg. 2016. PMID: 26230478 Review.
-
Patients with Carotid Intraplaque Hemorrhage Have Higher Incidence of Cerebral Microbleeds.Curr Probl Cardiol. 2023 Sep;48(9):101779. doi: 10.1016/j.cpcardiol.2023.101779. Epub 2023 May 11. Curr Probl Cardiol. 2023. PMID: 37172877 Review.
Cited by
-
Normalized intraplaque hemorrhage signal on MP-RAGE as a marker for acute ischemic neurological events.Neuroradiol J. 2022 Feb;35(1):112-118. doi: 10.1177/19714009211029263. Epub 2021 Jul 5. Neuroradiol J. 2022. PMID: 34224247 Free PMC article.
-
Cervical Carotid Plaque MRI : Review of Atherosclerosis Imaging Features and their Histologic Underpinnings.Clin Neuroradiol. 2021 Jun;31(2):295-306. doi: 10.1007/s00062-020-00987-y. Epub 2021 Jan 4. Clin Neuroradiol. 2021. PMID: 33398451 Review.
-
Studying the Factors of Human Carotid Atherosclerotic Plaque Rupture, by Calculating Stress/Strain in the Plaque, Based on CEUS Images: A Numerical Study.Front Neuroinform. 2020 Nov 24;14:596340. doi: 10.3389/fninf.2020.596340. eCollection 2020. Front Neuroinform. 2020. PMID: 33324188 Free PMC article.
-
Extracranial carotid plaque hemorrhage predicts ipsilateral stroke recurrence in patients with carotid atherosclerosis - a study based on high-resolution vessel wall imaging MRI.BMC Neurol. 2022 Jun 28;22(1):237. doi: 10.1186/s12883-022-02758-3. BMC Neurol. 2022. PMID: 35764942 Free PMC article.
-
Artificial Intelligence Algorithm-Based MRI in Evaluating the Treatment Effect of Acute Cerebral Infarction.Comput Math Methods Med. 2022 Jan 24;2022:7839922. doi: 10.1155/2022/7839922. eCollection 2022. Comput Math Methods Med. 2022. Retraction in: Comput Math Methods Med. 2023 Dec 6;2023:9794357. doi: 10.1155/2023/9794357. PMID: 35111236 Free PMC article. Retracted.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
