Widespread receptor-driven modulation in peripheral olfactory coding
- PMID: 32273438
- PMCID: PMC7443284
- DOI: 10.1126/science.aaz5390
Widespread receptor-driven modulation in peripheral olfactory coding
Abstract
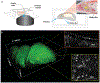
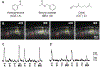
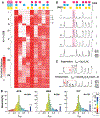
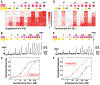
Olfactory responses to single odors have been well characterized but in reality we are continually presented with complex mixtures of odors. We performed high-throughput analysis of single-cell responses to odor blends using Swept Confocally Aligned Planar Excitation (SCAPE) microscopy of intact mouse olfactory epithelium, imaging ~10,000 olfactory sensory neurons in parallel. In large numbers of responding cells, mixtures of odors did not elicit a simple sum of the responses to individual components of the blend. Instead, many neurons exhibited either antagonism or enhancement of their response in the presence of another odor. All eight odors tested acted as both agonists and antagonists at different receptors. We propose that this peripheral modulation of responses increases the capacity of the olfactory system to distinguish complex odor mixtures.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

