Intravital imaging of mouse embryos
- PMID: 32273467
- PMCID: PMC7646360
- DOI: 10.1126/science.aba0210
Intravital imaging of mouse embryos
Abstract
Embryonic development is a complex process that is unamenable to direct observation. In this study, we implanted a window to the mouse uterus to visualize the developing embryo from embryonic day 9.5 to birth. This removable intravital window allowed manipulation and high-resolution imaging. In live mouse embryos, we observed transient neurotransmission and early vascularization of neural crest cell (NCC)-derived perivascular cells in the brain, autophagy in the retina, viral gene delivery, and chemical diffusion through the placenta. We combined the imaging window with in utero electroporation to label and track cell division and movement within embryos and observed that clusters of mouse NCC-derived cells expanded in interspecies chimeras, whereas adjacent human donor NCC-derived cells shrank. This technique can be combined with various tissue manipulation and microscopy methods to study the processes of development at unprecedented spatiotemporal resolution.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works.
Figures
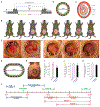
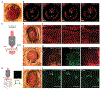
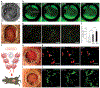
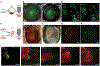
Comment in
-
Watching embryos develop.Nat Methods. 2020 Jun;17(6):560. doi: 10.1038/s41592-020-0864-2. Nat Methods. 2020. PMID: 32499621 No abstract available.
References
-
- Hadjantonakis AK, Dickinson ME, Fraser SE, Papaioannou VE, Nat. Rev. Genet 4, 613–625 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Di Cristofano A, Pesce B, Cordon-Cardo C, Pandolfi PP, Nat. Genet 19, 348–355 (1998). - PubMed
-
- Pantazis P, Supatto W, Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol 15, 327–339 (2014). - PubMed
-
- McDole K et al., Cell 175, 859–876.e33 (2018). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 HD039963/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R21 NS098176/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH104610/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R35 CA197616/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 HD045022/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R21 MH119813/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS110388/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R35 GM122465/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS083897/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS088538/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK119795/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA214300/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

