Multiple ecological processes underpin the eruptive dynamics of small mammals: House mice in a semi-arid agricultural environment
- PMID: 32274003
- PMCID: PMC7141066
- DOI: 10.1002/ece3.6145
Multiple ecological processes underpin the eruptive dynamics of small mammals: House mice in a semi-arid agricultural environment
Abstract
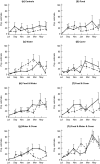
Mouse plagues are a regular feature of grain-growing regions, particularly in southern and eastern Australia, yet it is not clear what role various ecological processes play in the eruptive dynamics generating these outbreaks.This research was designed to assess the impact of adding food, water, and cover in all combinations on breeding performance, abundance, and survival of mouse populations on a typical cereal growing farm in northwestern Victoria.Supplementary food, water, and cover were applied in a 2 × 2 × 2 factorial design to 240 m sections of internal fence lines between wheat or barley crops and stubble/pasture fields over an 11-month period to assess the impact on mouse populations.We confirmed that mice were eating the additional food and were accessing the water provided. We did not generate an outbreak of mice, but there were some significant effects from the experimental treatments. Additional food increased population size twofold and improved apparent survival. Both water and cover improved breeding performance. Food and cover increased apparent survival.Our findings confirm that access to food, water, and cover are necessary for outbreaks, but are not sufficient. There remain additional factors that are important in generating mouse plagues, particularly in a climatically variable agricultural environment.
Keywords: abundance; breeding; food addition; mouse plague; survival.
© 2020 The Authors. Ecology and Evolution published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures







References
-
- Arthur, A. D. , Pech, R. P. , & Dickman, C. R. (2004). Habitat structure mediates the non‐lethal effects of predation on enclosed populations of house mice. Journal of Animal Ecology, 73, 867–877. 10.1111/j.0021-8790.2004.00864.x - DOI
-
- Arthur, A. D. , Pech, R. P. , & Dickman, C. R. (2005). Effects of predation and habitat structure on the population dynamics of house mice in large outdoor enclosures. Oikos, 108, 562–572. 10.1111/j.0030-1299.2005.13327.x - DOI
-
- Bomford, M. (1985). Food quality, diet and reproduction of house mice on irrigated cereal farms. PhD Thesis, Department of Zoology, Australian National University.
-
- Bomford, M. (1987a). Food and reproduction of wild house mice II. A field experiment to examine the effect of food availability and food quality on breeding in spring. Australian Wildlife Research, 14, 197–206.
-
- Bomford, M. (1987b). Food and reproduction of wild house mice III. Experiments on the breeding performance of caged house mice fed rice‐based diets. Australian Wildlife Research, 14, 207–218.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

