The Authors Reply
- PMID: 32274463
- PMCID: PMC7136343
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ekir.2019.12.005
The Authors Reply
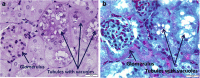
Figures
References
-
- van Kesteren P.C., Cubadda F., Bouwmeester H. Novel insights into the risk assessment of the nanomaterial synthetic amorphous silica, additive E551, in food. Nanotoxicology. 2015;9:442–452. - PubMed
-
- Tassinari R., Di Felice G., Butteroni C. Hazard identification of pyrogenic synthetic amorphous silica (NM-203) after sub-chronic oral exposure in rat: a multitarget approach. Food Chem Toxicol. 2020;137:111168. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

