A new microdialysis probe for continuous lactate measurement during fetal monitoring: Proof of concept in an animal model
- PMID: 32274792
- PMCID: PMC7540415
- DOI: 10.1111/aogs.13865
A new microdialysis probe for continuous lactate measurement during fetal monitoring: Proof of concept in an animal model
Abstract
Introduction: Cardiotocography (CTG) is currently the most commonly used method for intrapartum fetal monitoring during labor. However, a high false-positive rate of fetal acidosis indicated by CTG leads to an increase in obstetric interventions. We developed a microdialysis probe that is integrated into a fetal scalp electrode allowing continuous measurement of lactate subcutaneously, thus giving instant information about the oxygenation status of the fetus. Our aim was to establish proof of concept in an animal model using a microdialysis probe to monitor lactate subcutaneously.
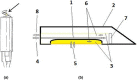
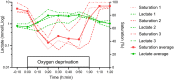
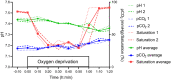
Material and methods: We performed an in vivo study in adult male wild-type Wistar rats. We modified electrodes used for CTG monitoring in human fetuses to incorporate a microdialysis membrane. Optimum flow rates for microdialysis were determined in vitro. For the in vivo experiment, a microdialysis probe was inserted into the skin on the back of the animal. De-oxygenation and acidosis were induced by lowering the inspiratory oxygen pressure. Oxygenation and heart rate were monitored. A jugular vein cannula was inserted to draw blood samples for analysis of lactate, pH, pco2 , and saturation. Lactate levels in dialysate were compared with plasma lactate levels.
Results: Baseline blood lactate levels were around 1 mmol/L. Upon de-oxygenation, oxygen saturation fell to below 40% for 1 h and blood lactate levels increased 2.5-fold. Correlation of dialysate lactate levels with plasma lactate levels was 0.89 resulting in an R2 of .78 in the corresponding linear regression.
Conclusions: In this animal model, lactate levels in subcutaneous fluid collected by microdialysis closely reflected blood lactate levels upon transient de-oxygenation, indicating that our device is suitable for subcutaneous measurement of lactate. Microdialysis probe technology allows the measurement of multiple compounds in the dialysate, such as glucose, albumin, or inflammatory mediators, so this technique may offer the unique possibility to shed light on fetal physiology during the intrapartum period.
Keywords: cardiotocography; cesarean; delivery; fetal acidosis; fetal monitoring; fetal scalp electrode; lactate; prenatal care.
© 2020 The Authors. Acta Obstetricia et Gynecologica Scandinavica published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Nordic Federation of Societies of Obstetrics and Gynecology (NFOG).
Conflict of interest statement
Th. Cremers is CEO of Can Holding BV and KD Huinink is CEO of Brainlink BV. The other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Continuous intrapartum pH, pO2, pCO2, and SpO2 monitoring.Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am. 1999 Dec;26(4):671-93. doi: 10.1016/s0889-8545(05)70106-6. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am. 1999. PMID: 10587962 Review.
-
The prediction of fetal acidosis by means of intrapartum fetal pulse oximetry.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1999 Jan;180(1 Pt 1):73-81. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(99)70153-5. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1999. PMID: 9914582
-
Scalp blood lactate for intra-partum assessment of fetal metabolic acidosis.Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2011 Oct;90(10):1107-14. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0412.2011.01237.x. Epub 2011 Aug 29. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2011. PMID: 21751970
-
STAN S21 fetal heart monitor for fetal surveillance during labor: an observational study in 637 patients.J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2004 Jun;15(6):400-7. doi: 10.1080/14767050410001727404. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2004. PMID: 15280112
-
[Fetal scalp blood sampling for pH and lactate measurement during labour].J Gynecol Obstet Biol Reprod (Paris). 2008 Feb;37 Suppl 1:S65-71. doi: 10.1016/j.jgyn.2007.11.012. Epub 2008 Jan 7. J Gynecol Obstet Biol Reprod (Paris). 2008. PMID: 18179877 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Frequency of fetal blood sampling, delivery mode and neonatal outcome after revised CTG-classification and updated lactate meter in Sweden: An observational study.Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2025 Apr;104(4):676-684. doi: 10.1111/aogs.15063. Epub 2025 Feb 7. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2025. PMID: 39917811 Free PMC article.
-
Intradermal Lactate Monitoring Based on a Microneedle Sensor Patch for Enhanced In Vivo Accuracy.ACS Sens. 2024 Jun 28;9(6):3115-3125. doi: 10.1021/acssensors.4c00337. Epub 2024 May 22. ACS Sens. 2024. PMID: 38778463 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alfirevic Z, Devane D, Gyte GM. Continuous cardiotocography (CTG) as a form of electronic fetal monitoring (EFM) for fetal assessment during labour. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013;5:CD006066. - PubMed
-
- Van den Berg P, Schmidt S, Gesche J, Saling E. Fetal distress and the condition of the newborn using cardiotocography and fetal blood analysis during labour. Br J Obstet Gynaecol. 1987;94(1):72‐75. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

