Structural and functional divergence of GDAP1 from the glutathione S-transferase superfamily
- PMID: 32274853
- PMCID: PMC9394736
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.202000110R
Structural and functional divergence of GDAP1 from the glutathione S-transferase superfamily
Abstract
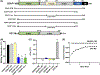
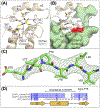
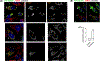
Mutations in ganglioside-induced differentiation-associated protein 1 (GDAP1) alter mitochondrial morphology and result in several subtypes of the inherited peripheral neuropathy Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease; however, the mechanism by which GDAP1 functions has remained elusive. GDAP1 contains primary sequence homology to the GST superfamily; however, the question of whether GDAP1 is an active GST has not been clearly resolved. Here, we present biochemical evidence, suggesting that GDAP1 has lost the ability to bind glutathione without a loss of substrate binding activity. We have revealed that the α-loop, located within the H-site motif is the primary determinant for substrate binding. Using structural data of GDAP1, we have found that critical residues and configurations in the G-site which canonically interact with glutathione are altered in GDAP1, rendering it incapable of binding glutathione. Last, we have found that the overexpression of GDAP1 in HeLa cells results in a mitochondrial phenotype which is distinct from oxidative stress-induced mitochondrial fragmentation. This phenotype is dependent on the presence of the transmembrane domain, as well as a unique hydrophobic domain that is not found in canonical GSTs. Together, we data point toward a non-enzymatic role for GDAP1, such as a sensor or receptor.
Keywords: X-ray crystallography; ganglioside-induced differentiation-associated protein 1; mitochondria; oxidative stress; structural biology.
© 2020 Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

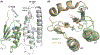



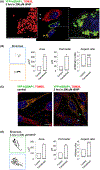
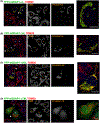
References
-
- Kazamel M, Boes CJ. Charcot Marie Tooth disease (CMT): historical perspectives and evolution. J Neurol. 2015;262:801–805. - PubMed
-
- Laura M, Pipis M, Rossor AM, Reilly MM. Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease and related disorders: an evolving landscape. Curr Opin Neurol. 2019;32(5):641–650. - PubMed
-
- Rossor AM, Lu CH, Petzold A, et al. Plasma neurofilament heavy chain is not a useful biomarker in Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease. Muscle Nerve. 2016;53:972–975. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

