COVID-19 in Italy: impact of containment measures and prevalence estimates of infection in the general population
- PMID: 32275287
- PMCID: PMC7975916
- DOI: 10.23750/abm.v91i3-S.9511
COVID-19 in Italy: impact of containment measures and prevalence estimates of infection in the general population
Abstract
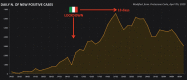
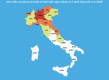
Since the beginning of the COVID-19 epidemic in Italy, the Italian Government implemented several restrictive measures to contain the spread of the infection. Data shows that, among these measures, the lockdown implemented as of 9 March had a positive impact, in particular the central and southern regions of Italy, while other actions appeared to be less effective. When the true prevalence of a disease is unknown, it is possible estimate it, based on mortality data and the assumptive case-fatality rate of the disease. Given these assumptions, the estimated period-prevalence of COVID-19 in Italy varies from 0.35% in Sicity to 13.3% in Lombardy.
Conflict of interest statement
Each author declares that he or she has no commercial associations (e.g. consultancies, stock ownership, equity interest, patent/licensing arrangement etc.) that might pose a conflict of interest in connection with the submitted article
Figures
References
-
- Dipartimento della Protezione Civile. COVID-19 Italia - Monitoraggio della situazione. Aggiornato al 7/4/2020. http://www.protezionecivile.gov.it. / (accessed 08.04.20)
-
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC) Situation update. 6 april 2020 https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/en/geographical-distribution-2019-ncov-cases. (accessed 08.04.20)
-
- Signorelli C, Odone A, Oradini-Alacreu A, Pelissero G. Universal Health Coverage in Italy: lights and shades of the Italian National Health Service which celebrated its 40th anniversary. Health Policy. 2020 Jan;124(1):69–74. - PubMed
-
- Boccia S, Ricciardi W, Ioannidis JPA. What Other Countries Can Learn From Italy During the COVID-19 Pandemic. JAMA Intern Med. 2020 Apr 7 doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.1447. [Epub ahead of print] - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

