Aerosol and Surface Distribution of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 in Hospital Wards, Wuhan, China, 2020
- PMID: 32275497
- PMCID: PMC7323510
- DOI: 10.3201/eid2607.200885
Aerosol and Surface Distribution of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 in Hospital Wards, Wuhan, China, 2020
Abstract
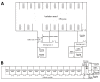
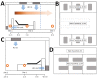
To determine distribution of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 in hospital wards in Wuhan, China, we tested air and surface samples. Contamination was greater in intensive care units than general wards. Virus was widely distributed on floors, computer mice, trash cans, and sickbed handrails and was detected in air ≈4 m from patients.
Keywords: 2019 novel coronavirus disease; COVID-19; China; SARS-CoV-2; Wuhan; aerosol; coronavirus disease; exposure risk; hospital-associated infection; medical staff protection; respiratory infections; severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; viruses; zoonoses.
Figures
Comment in
-
Protecting healthcare workers from inhaled SARS-CoV-2 virus.Occup Med (Lond). 2020 Jul 17;70(5):335-337. doi: 10.1093/occmed/kqaa077. Occup Med (Lond). 2020. PMID: 32352523 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Coronavirus disease 2019. (COVID-19) situation report-71 [cited 2020 Mar 30]. https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/situatio...
-
- Ong SWX, Tan YK, Chia PY, Lee TH, Ng OT, Wong MSY, et al. Air, surface environmental, and personal protective equipment contamination by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) from a symptomatic patient. JAMA. 2020; Epub ahead of print. 10.1001/jama.2020.3227 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

