Compassionate Use of Remdesivir for Patients with Severe Covid-19
- PMID: 32275812
- PMCID: PMC7169476
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa2007016
Compassionate Use of Remdesivir for Patients with Severe Covid-19
Abstract
Background: Remdesivir, a nucleotide analogue prodrug that inhibits viral RNA polymerases, has shown in vitro activity against SARS-CoV-2.
Methods: We provided remdesivir on a compassionate-use basis to patients hospitalized with Covid-19, the illness caused by infection with SARS-CoV-2. Patients were those with confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection who had an oxygen saturation of 94% or less while they were breathing ambient air or who were receiving oxygen support. Patients received a 10-day course of remdesivir, consisting of 200 mg administered intravenously on day 1, followed by 100 mg daily for the remaining 9 days of treatment. This report is based on data from patients who received remdesivir during the period from January 25, 2020, through March 7, 2020, and have clinical data for at least 1 subsequent day.
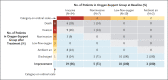
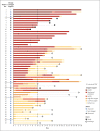
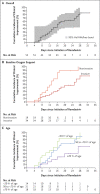
Results: Of the 61 patients who received at least one dose of remdesivir, data from 8 could not be analyzed (including 7 patients with no post-treatment data and 1 with a dosing error). Of the 53 patients whose data were analyzed, 22 were in the United States, 22 in Europe or Canada, and 9 in Japan. At baseline, 30 patients (57%) were receiving mechanical ventilation and 4 (8%) were receiving extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. During a median follow-up of 18 days, 36 patients (68%) had an improvement in oxygen-support class, including 17 of 30 patients (57%) receiving mechanical ventilation who were extubated. A total of 25 patients (47%) were discharged, and 7 patients (13%) died; mortality was 18% (6 of 34) among patients receiving invasive ventilation and 5% (1 of 19) among those not receiving invasive ventilation.
Conclusions: In this cohort of patients hospitalized for severe Covid-19 who were treated with compassionate-use remdesivir, clinical improvement was observed in 36 of 53 patients (68%). Measurement of efficacy will require ongoing randomized, placebo-controlled trials of remdesivir therapy. (Funded by Gilead Sciences.).
Copyright © 2020 Massachusetts Medical Society.
Figures
Comment in
-
Remdesivir in covid-19.BMJ. 2020 Apr 22;369:m1610. doi: 10.1136/bmj.m1610. BMJ. 2020. PMID: 32321732 No abstract available.
-
Coronavirus drugs trials must get bigger and more collaborative.Nature. 2020 May;581(7807):120. doi: 10.1038/d41586-020-01391-9. Nature. 2020. PMID: 32405023 No abstract available.
-
Compassionate Use of Remdesivir in Covid-19.N Engl J Med. 2020 Jun 18;382(25):e101. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2015312. Epub 2020 May 15. N Engl J Med. 2020. PMID: 32412705 No abstract available.
-
Compassionate Use of Remdesivir in Covid-19.N Engl J Med. 2020 Jun 18;382(25):e101. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2015312. Epub 2020 May 15. N Engl J Med. 2020. PMID: 32412706 No abstract available.
-
Compassionate Use of Remdesivir in Covid-19.N Engl J Med. 2020 Jun 18;382(25):e101. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2015312. Epub 2020 May 15. N Engl J Med. 2020. PMID: 32412707 No abstract available.
-
Compassionate Use of Remdesivir in Covid-19.N Engl J Med. 2020 Jun 18;382(25):e101. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc2015312. Epub 2020 May 15. N Engl J Med. 2020. PMID: 32412708 No abstract available.
-
Development of passive immunity against SARS-CoV-2 for management of immunodeficient patients-a perspective.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2020 Jul;146(1):58-60. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2020.04.043. Epub 2020 May 12. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32413374 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Mahase E, Kmietowicz Z. Covid-19: doctors are told not to perform CPR on patients in cardiac arrest. BMJ 2020;368:m1282-m1282. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
